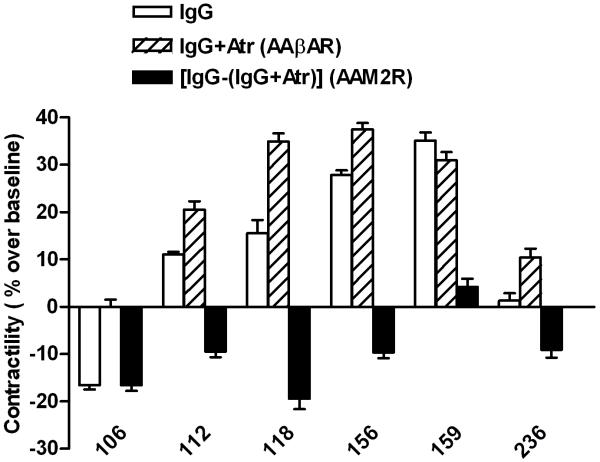
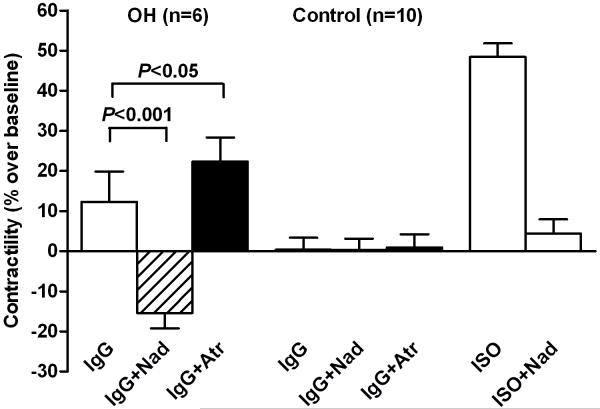
Figure 1. Effects of IgG from the 6 orthostatic hypotension patients on Purkinje contractility.
A. Each value represents the mean ± SD of 15 consecutive contractions and was measured once the preparation had stabilized. The data are expressed as percent above basal levels of the buffer control. The IgG alone shows net activity. An increase in contractility over baseline with IgG plus muscarinic blocker atropine (Atr) represented the βAR effect of IgG (AAβAR). The difference in IgG effect on contractility between the presence and absence of atropine was a surrogate marker of the M2R inhibitory effect of IgG (AAM2R). The co-presence of atropine demonstrates that βAR activity was impaired partially by concurrent M2R inhibitory effects in 4 of the 6 patients. Patient 106 has marked M2R dominance while patient 159 is βAR dominant. B. The mean effect of IgG from the 6 patients on Purkinje contractility. The βAR activity of the IgG was measured as effect of IgG plus atropine (Atr) and M2R activity as IgG plus the non-selective β-blocker nadolol (Nad). The effect of IgG from 10 control subjects and the positive isoproterenol (ISO) control are also shown.