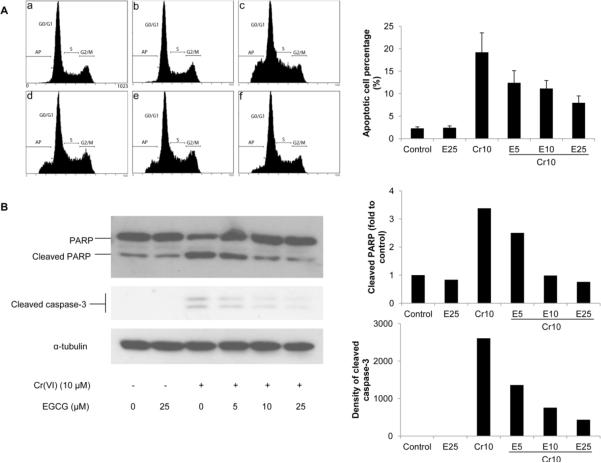
Fig. 2.
EGCG inhibits Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis. BEAS-2B cells were treated with 10 μM Cr(VI) and increasing concentrations of EGCG (5–25 μM) for 24 h. A, The cells were collected and stained with propidium iodide. DNA content was analyzed by flow cytometry, and a representative cell cycle profile was shown in the upper panel. (a) control, (b) 25 μM EGCG, (b) 10 μM Cr(VI), (d) 10 μM Cr(VI) + 5 μM EGCG, (e) 10 μM Cr(VI) + 10 μM EGCG, and (f) 10 μM Cr(VI) + 25 μM EGCG. The bottom panel is the apoptotic cell percentage. B, The cells were lysed and cleavage of PARP and caspase-3 were measured by Western blot. The left panels are representative blots while the right panels are the densitometric data.