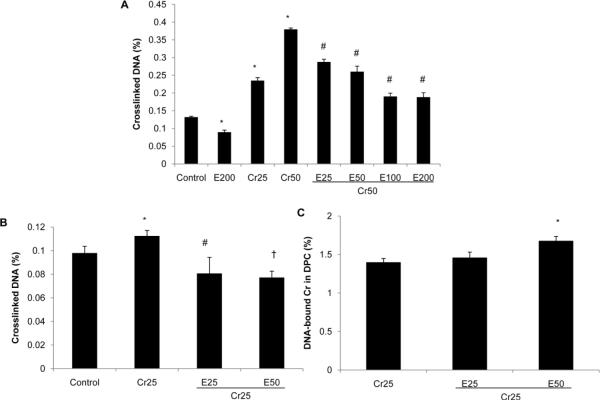
Fig. 4.
EGCG decreases Cr(VI)-induced DNA-protein cross-links (DPC). EBV-BL cells were treated with selected concentrations of Cr(VI) and EGCG in the presence or absence of radiolabeled 51Cr(VI) for 24 h. Cells were then collected and assayed for DPC as described in the Materials and Methods section. The percentage of cross-linked DNA is the ratio of SDS-precipitable DNA to total DNA. The percentage of DNA-bound Cr is the ratio of radioactivity in SDS-precipitable DNA to that in total DNA. Values are Mean ± SD (n = 3). A, Cr(VI) significantly increased DPC and addition of EGCG dose-dependently decreased Cr(VI)-induced DPC formation. *P < 0.01 vs control, #P < 0.01 vs Cr50. B, EGCG abrogated Cr(VI)-induced DPC formation in EBV-BL cells. *P < 0.05 vs control, #P < 0.01 vs Cr25, †P < 0.01 vs Cr25. C, EGCG does not inhibit Cr(III) cross-linking to DNA. *P < 0.01 vs Cr25.