Fig. 5.
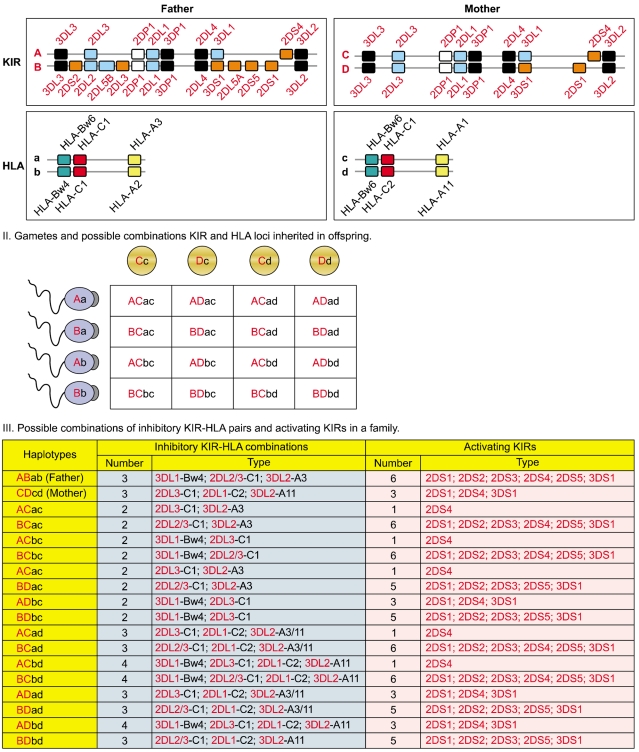
KIR and HLA gene families are unlinked and located on different human chromosomes, 19 and 6 respectively. Both gene families evolve rapidly and feature substantial variation between haplotypes in the number and type of genes. Panel I illustrates variation between parents in KIR and HLA haplotypes. Panel II illustrates all four possible types of gametes from each parent assorted with different combination of one KIR haplotype and one HLA haplotype. Random associations of gametes form zygotes of the next generation carrying one of the 16 possible combinations of paternal and maternal KIR and HLA haplotypes, producing substantial diversity between offspring in the number and type of inhibitory KIR-HLA combinations and activating KIR genes inherited (Panel III).