Abstract
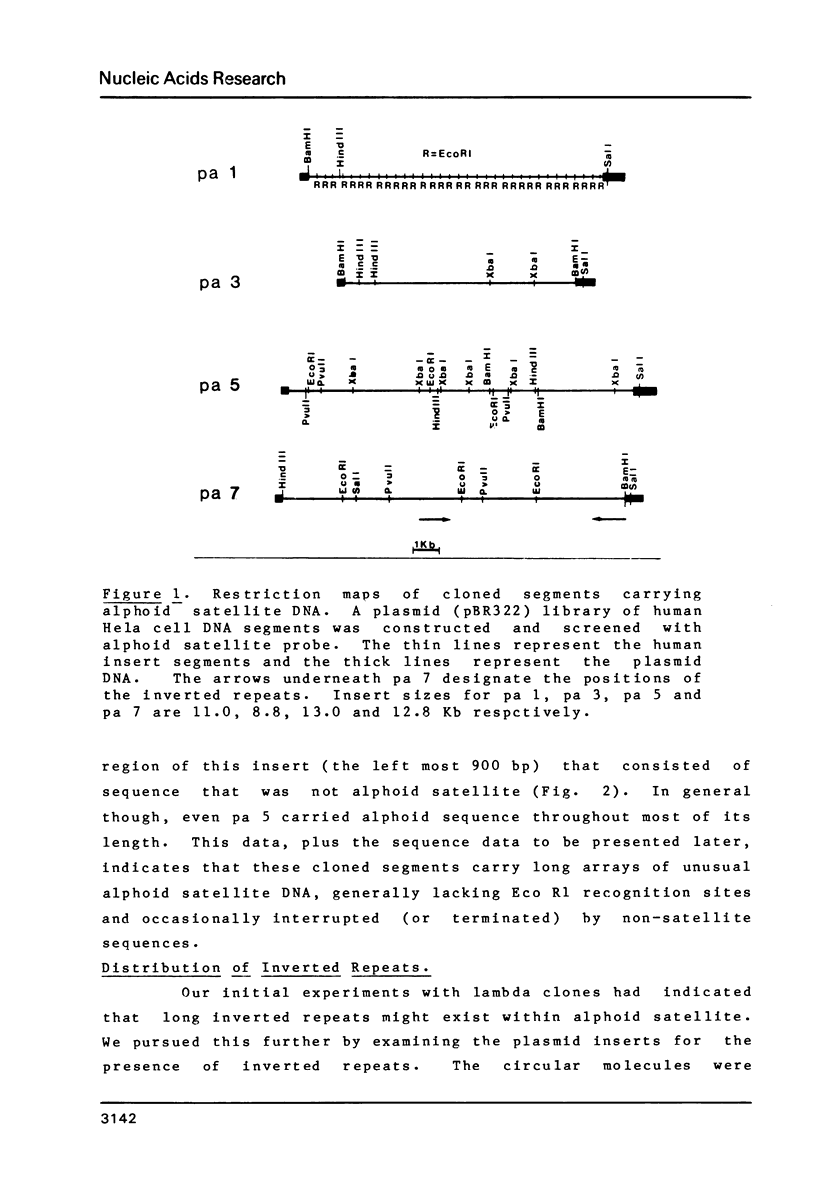
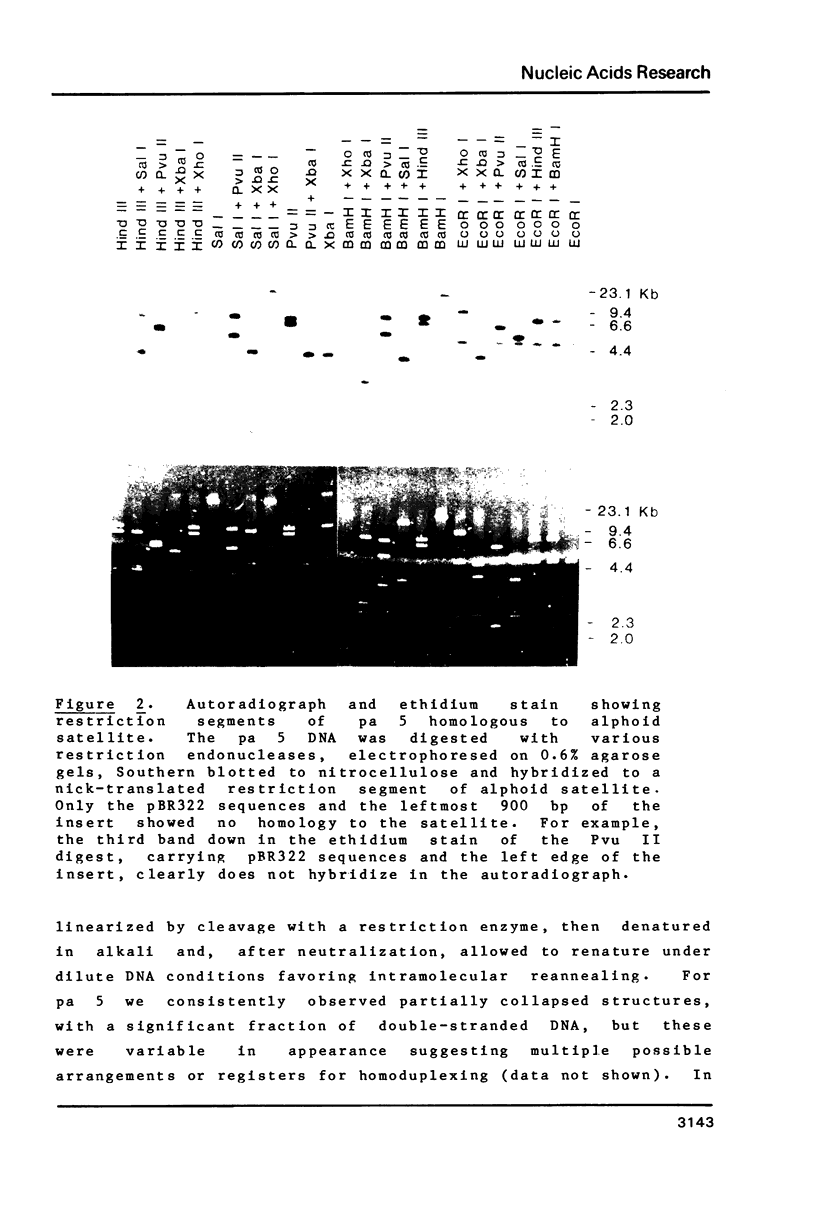
The sequence organization of cloned segments of Human DNA carrying unusual domains of alphoid satellite was studied by restriction mapping, electron microscopy and base sequence analysis. In some cases restriction mapping revealed the absence of the typical 340 bp EcoR 1 dimer, although blot hybridizations showed the extensive presence of alphoid satellite. A variant monomeric construction was demonstrated by DNA sequencing. Furthermore, inverted repeats within these domains were detected by electron microscopy. In one case these were shown to be the result of interruptions in the satellite sequence by members of a family of repetitive, conserved elements.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. W., Kaufman R. E., Kretschmer P. J., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. A family of long reiterated DNA sequences, one copy of which is next to the human beta globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6113–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp R. S., Mitchell A. R., Buckland R. A., Bostock C. J. Specific arrangements of human satellite III DNA sequences in human chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1979 Feb 21;71(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00292820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. A. The specific organisation of satellite DNA sequences on the X-chromosome of Mus musculus: partial independence of chromosome evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):781–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D. L. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:121–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Brutlag D. One of the copia genes is adjacent to satellite DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Hindley J. Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3177–3197. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Crampton J. M., Williamson R. Organization of a family of highly repetitive sequences within the human genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newt Notophthalmus. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):649–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L., Furlong C., Gillespie D., Kurnit D. DNA sequence of baboon highly repeated DNA: evidence for evolution by nonrandom unequal crossovers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L., Gillespie D. Restriction site periodicities in highly repetitive DNA of primates. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):805–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90487-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D. Newly evolved repeated DNA sequences in primates. Science. 1977 May 20;196(4292):889–891. doi: 10.1126/science.870965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliker A. J., Appels R., Schalet A. The genetic analysis of D. melanogaster heterochromatin. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):607–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H. Organization and heterogeneity of sequences within a repeating unit of human Y chromosome deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3343–3353. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M., Maio J. J. Variable satellite DNA's in the African green monkey Cercopithecus aethiops. Chromosoma. 1974 May 10;45(4):387–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00283385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Singer M. F. Structural organization of alpha-satellite DNA in a single monkey chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):323–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Collins M., Rubin G. M. FB elements are the common basis for the instability of the wDZL and wC Drosophila mutations. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):551–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90252-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Rubin G. M. The unstable wDZL mutation of Drosophila is caused by a 13 kilobase insertion that is imprecisely excised in phenotypic revertants. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., McKenna W. G., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. II. The KpnI families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):127–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00286020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J., Brown F. L., Musich P. R. Toward a molecular paleontology of primate genomes. I. The HindIII and EcoRI dimer families of alphoid DNAs. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):103–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00286019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maio J. J. DNA strand reassociation and polyribonucleotide binding in the African green monkey, Cercopithecus aethiops. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T., Hsu H., Thayer R. E., Singer M. F. Organization of African green monkey DNA at junctions between alpha-satellite and other DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musich P. R., Brown F. L., Maio J. J. Highly repetitive component alpha and related alphoid DNAs in man and monkeys. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):331–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00292688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence analysis of a Drosophila foldback transposable element rearrangement. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(1):107–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00333002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence of a foldback transposable element in Drosophila. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):201–204. doi: 10.1038/297201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizes G., Pages M., Lecou C. The organisation of the long range periodicity calf satellite DNA I variants as revealed by restriction enzyme analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3779–3792. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Singer M., Rosenberg M. Highly reiterated sequences of SIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIANSIMIAN. Science. 1978 Apr 28;200(4340):394–402. doi: 10.1126/science.205944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Deininger P. L., Houck C. M., Schmid C. W. A dimer satellite sequence in bonnet monkey DNA consists of distinct monomer subunits. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 15;136(2):151–167. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeckpeper B. J., Willard H. F., Smith K. D. Isolation and characterization of cloned human DNA fragments carrying reiterated sequences common to both autosomes and the X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1853–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Donehower L. Highly repeated DNA of the baboon: organization of sequences homologous to highly repeated DNA of the African green monkey. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90488-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer R. E., Singer M. F., McCutchan T. F. Sequence relationships between single repeat units of highly reiterated African Green monkey DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):169–181. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Macgregor H. C., Erba H. P. Satellite DNA is transcribed on lampbrush chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):686–688. doi: 10.1038/283686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]