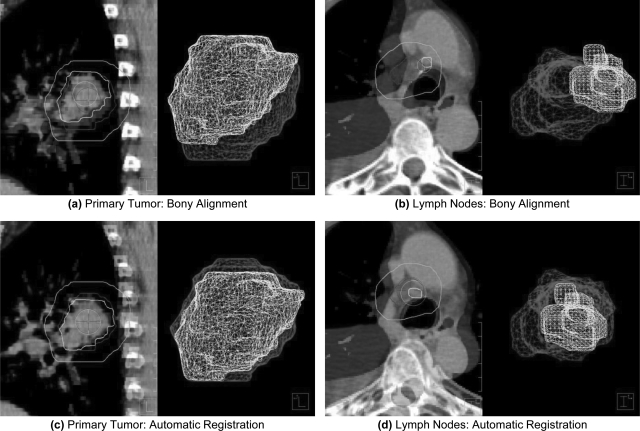
Figure 1.
Overlay image showing the registration of targets from reference and secondary CTs from two different patients. Images were initially aligned using bony-anatomy (a)–(b). Pleural effusion likely contributed to the initial misalignment of an involved lymph node in (b). Automatic, rigid registration improved the localization of both the primary tumor (c) and involved lymph nodes (d) for patients in this study. The smaller surface meshes (foreground) represent targets from weekly CT images, whereas the larger surface meshes (background) represent targets from the initial planning CT. An additional contour is provided to demonstrate the registration volume obtained by a 10 mm isotropic expansion of targets from the planning CT.