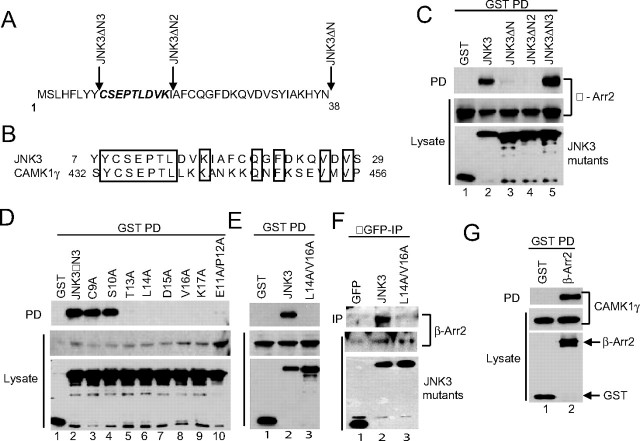
FIGURE 2.
Mapping residues critical for JNK3 binding to β-arrestin-2. A, 38-amino acid N-terminal extension of JNK3. The positions of the N-terminal deletion mutants are indicated. The residues mutated to Ala are in bold italics. B, alignment of the N-terminal sequences of human JNK3 and CAMK1γ. Conserved residues are boxed. Numbers refer to amino acids. C–E, constructs expressing GST or GST-tagged JNK3 mutants were introduced into COS-7 cells together with an expression vector for FLAG-β-arrestin-2. GST-containing complexes were isolated from cell lysates with glutathione-Sepharose beads, and the β-arrestin-2 present in the pull-down (PD) was examined by immunoblot using M2 antibody. The expression of the JNK3 deletions and β-arrestin-2 was examined by immunoblotting the lysates with anti-GST and M2 antibodies, respectively. F, constructs expressing GFP, GFP-JNK3, and GFP-JNK3(L14A/V16A) were introduced into 293T cells and JNK3-containing complexes isolated using anti-GFP antibodies. The presence of endogenous β-arrestin-2 in the precipitates (IP) was detected using an anti-β-arrestin antibody. The expression of the JNK3 proteins and β-arrestin-2 was examined by immunoblotting the lysates with anti-GFP and anti-β-arrestin antibodies, respectively. G, constructs expressing GST or GST-tagged β-arrestin-2 were introduced into COS-7 cells together with an expression vector for Myc-tagged CAMK1γ. GST-containing complexes were isolated from cell lysates with glutathione-Sepharose beads, and the CAMK1γ present in the pull-down (PD) was examined by immunoblot using anti-Myc antibody. Experiments were performed either two or three times and representative immunoblots are shown.