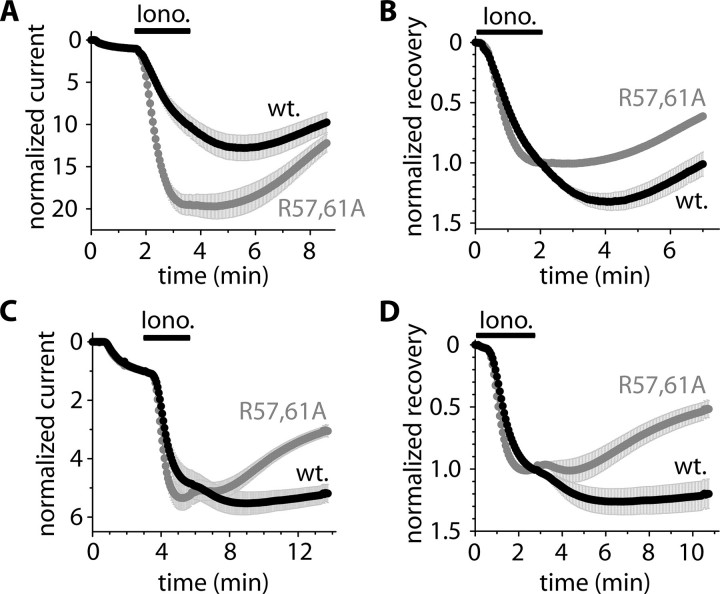
FIGURE 2.
The microinjection of recombinant GST-h14-3-3η protein inhibits the activation of mouse TRESK and delays the recovery from activation of both human and mouse TRESK channels. A, normalized currents of two groups of oocytes microinjected with 50 nl of GST-h14-3-3η (wild type, wt., black curve) or R57A,R61A mutant GST-h14-3-3η fusion protein (gray curve). The cells were coexpressing mouse TRESK with R57A,R61A 14-3-3η (in both groups). Extracellular [K+] was increased from 2 to 80 mm, and the oocytes were challenged with ionomycin (Iono., 0.5 μm, as indicated by the horizontal black bar) 108–248 min after the microinjection of the proteins. B, normalized recovery was calculated from the same recordings as represented in panel A. C and D, a similar microinjection experiment as in A and B was performed with human TRESK in another oocyte preparation. The proteins were microinjected 188–236 min before the application of ionomycin.