FIGURE 6.
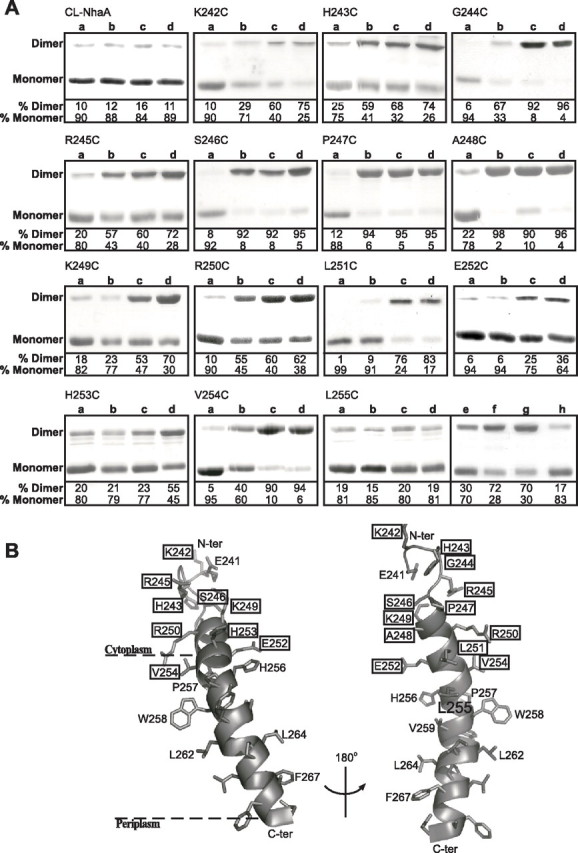
Intermolecular cross-linking between NhaA monomers with a single Cys replacement. High pressure membrane vesicles were isolated from TA16 cells expressing the various NhaA mutants from pCL-HAH4. A, the membranes were untreated (Lanes a) or treated with the cross-linkers o-PDM (Lanes b), p-PDM (Lanes c), and BMH (Lanes d) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Proteins were then purified, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and Coomassie Blue-stained, and the densities of the bands were determined. When intermolecular cross-linking takes place, a band, corresponding in mobility to that of the NhaA dimer, appears in SDS-PAGE. The extent of intermolecular cross-linking is expressed in percentage of dimers (100% = monomers + dimers). Panel L255C, Lanes a–d, as above; Lanes e–h, non-reducing conditions in the gel; Lane e, untreated; Lane f, diamide; Lanes g and h, MTS-2-MTS and o-PDM, respectively. Several concentrations of each reagent were tested with similar results. The standard deviation was between 5 and 10%. B, a ribbon representation of TMS IX and the proximal part of loop VIII–IX. The single letter amino acid codes are used, and the location in the amino acid sequence is indicated by a number. The various levels of cross-linking are depicted in rectangles of thin (partial cross-linking with BMH only), medium (partial cross-linking with two or all three reagents), and thick (efficient cross-linking with all three reagents) lines. The unique cross-linking behavior of Leu255 is represented in a filled black rectangle. The presentation was generated using PyMOL.
