FIGURE 5.
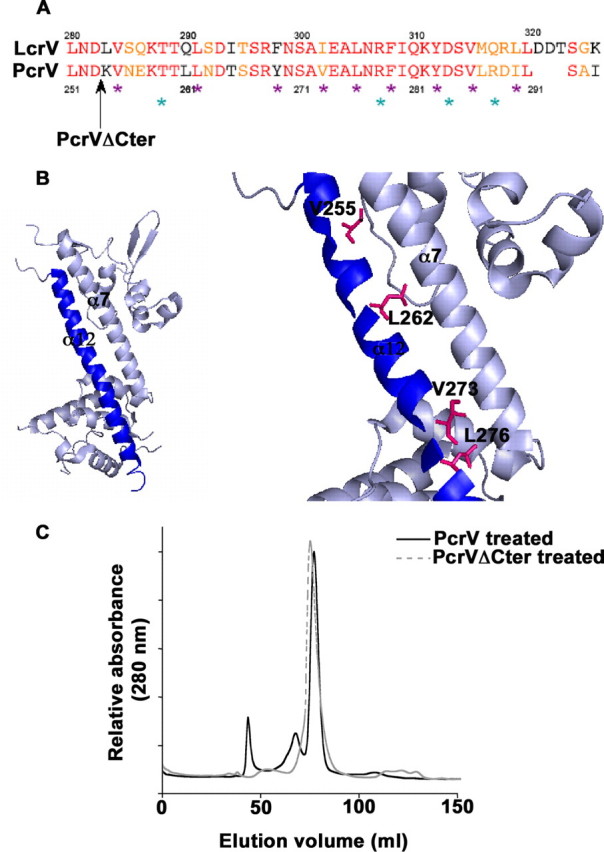
The conserved C-terminal α12 helix plays a key role in the protein functionality. A, alignment of LcrV and PcrV C-terminal α12 helix sequences. Identical residues and similar residues are shown in red and orange, respectively. The black arrow shows the end of the protein sequence of the PcrVΔCter mutant. Mutated residues are outlined by violet stars for hydrophobic residues (Val255, Leu262, Tyr269, Val273, Leu276, Phe279, Tyr283, Val286, and Ile290) and cyan stars for hydrophilic residues (Thr259, Arg278, Asp284, and Arg288). B, schematic of the LcrV structure (PDB 1R6F (36)). The C-terminal α12 helix is represented in blue. Zoom on the area of interest: mutated residues affecting Pseudomonas cytotoxicity (Val255, Leu262, Leu276, and Val273) are shown by stick representation. C, capacity of oligomerization of PcrVΔCter was assessed by pH treatment followed by size exclusion chromatography. Chromatogram of PcrVΔCter is overlaid with the chromatogram of pH-treated wild-type PcrV. PcrVΔCter is inefficient in forming the high molecular weight oligomeric state of PcrV.
