FIGURE 2.
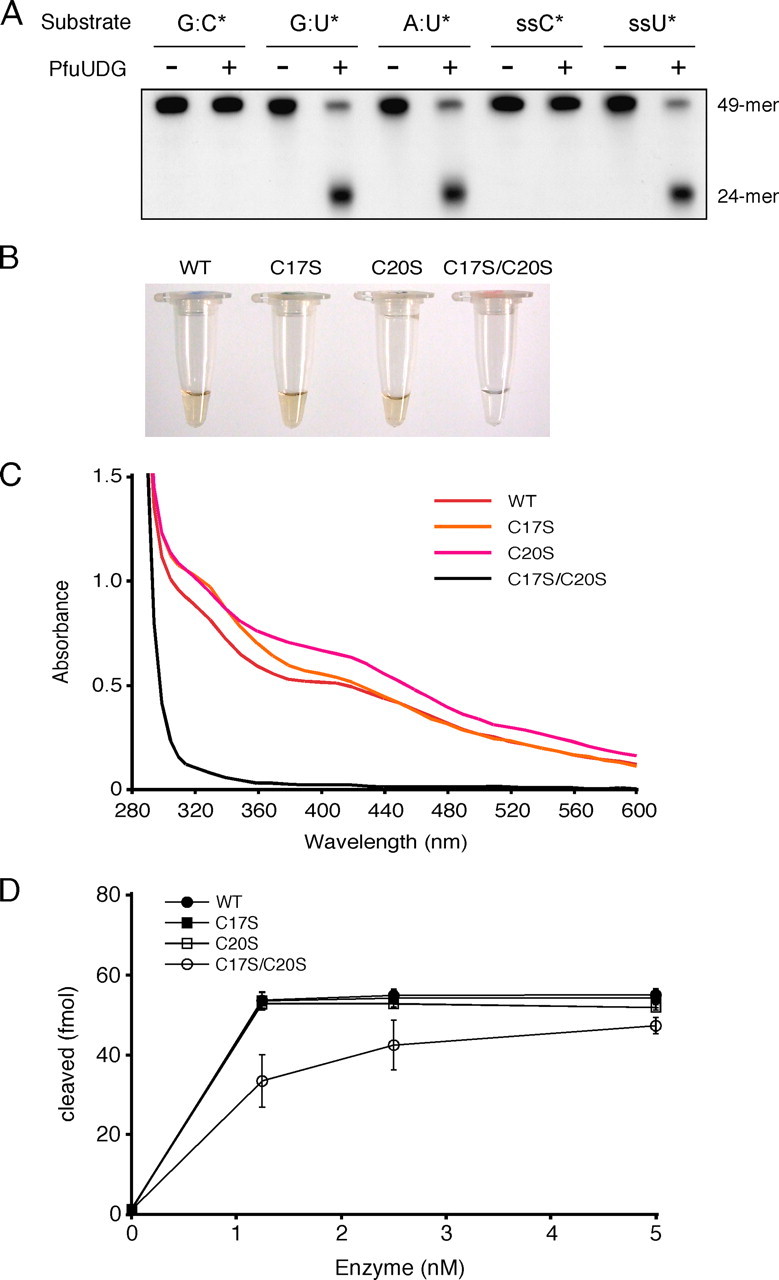
Biochemical properties of PfuUDG. A, the substrate specificity of PfuUDG was examined by using a synthetic 49-mer oligonucleotide containing a uracil base at the center. Wild-type PfuUDG (20 fmol) was incubated with 100 fmol of the double-stranded DNA substrates containing G:C*, G:U*, and A:U* base pairs (the asterisk indicates the 32P-labeled oligonucleotide) in the reaction, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A single-stranded (ss) DNA was also tested in the same manner as the double-stranded DNA substrates. B, the colors of the purified wild-type (WT) and mutant (C17S, C20S, and C17S/C20S) PfuUDG protein solutions at a concentration of 180 μm are shown. C, the UV-visible absorption spectra (280-600 nm) of the PfuUDG proteins at a concentration of 180 μm are shown. D, comparison of the enzyme activities of the wild-type and mutant (C17S, C20S, and C17S/C20S) PfuUDGs. Various amounts of the PfuUDG proteins, as indicated, were incubated with 100 fmol of the uracil-containing DNA substrate (G:U*) in the reaction, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The uracil excision efficiency is plotted as a function of the enzyme concentration.
