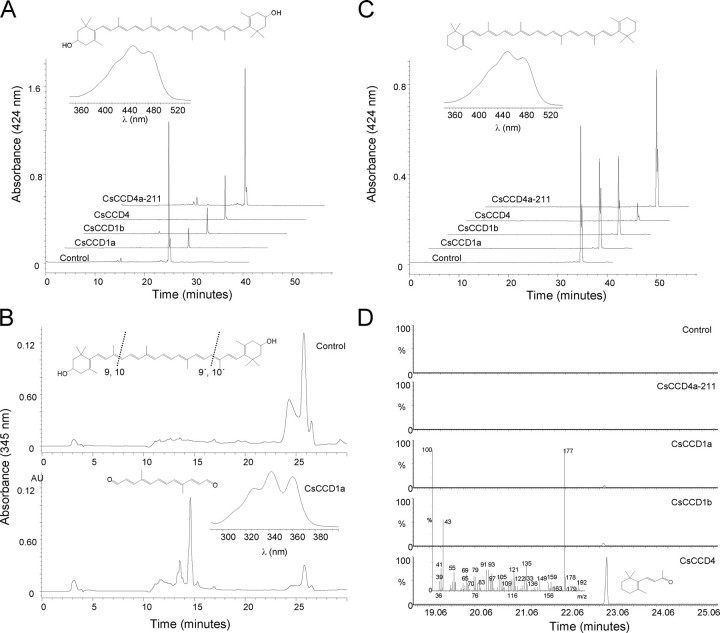
FIGURE 2.
Expression of CsCCD enzymes in carotenoid-producing strains of E. coli. E. coli engineered to accumulate the carotenoids β-carotene and zeaxanthin were transformed with an arabinose-inducible recombinant vector for CsCCD1a, CsCCD1b, CsCCD4a-211, and CsCCD4. A, representative HPLC elution profiles of zeaxanthin levels without (control) and with induction of CsCCD1a, CsCCD1b, CsCCD4a-211, and CsCCD4 expression. Inset, on-line spectrum and structure of zeaxanthin. B, chromatogram at absorbance of 345 nm of the zeaxanthin + CsCCD1a combination with the cleavage product peak at 15 min present in the lower chromatogram. The absorption maximum of the obtained product was consistent with that of C14 dialdehyde reported previously (3). Inset, in the upper part the structure of zeaxanthin is shown and the 9,10 and 9′,10′ double bonds are indicated; in the lower part the on-line spectrum and structure of the obtained product after a 9,10(9′,10′) cleavage. C, representative HPLC elution profiles of β-carotene levels without (control) and with induction of CsCCD1a, CsCCD1b, CsCCD4a-211, and CsCCD4 expression. Inset, on-line spectrum and structure of β-carotene. D, GC/MS analysis showing β-ionone emitted by bacteria following induction of CsCCD1a, CsCCD1b, CsCCD4a-211, and CsCCD4 expression. Inset, in the upper part the structure of β-carotene is shown and the 9,10 and 9′,10′ double bonds are indicated, in the lower part the mass spectrum of the observed of β-ionone product. Controls are representative chromatograms from uninduced cultures.