FIGURE 2.
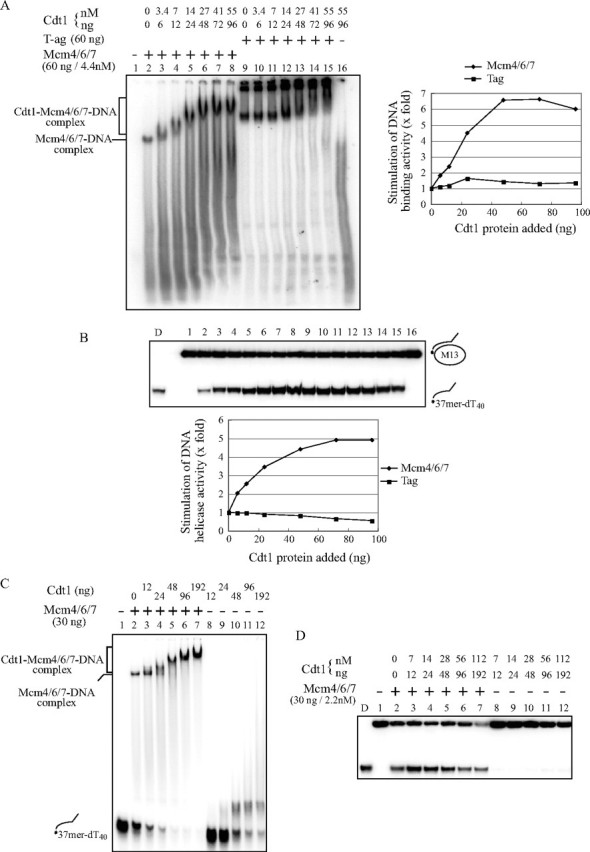
Cdt1 stimulates DNA binding and helicase activities of Mcm4/6/7. DNA binding (A and C) and helicase (B and D) activities were examined with a constant amount of Mcm4/6/7 (60 ng/4.4 nm (A and B) or 30 ng/2.2 nm (C and D)) and various amounts of Cdt1 protein purified from insect cells (A and B) or from E. coli (C and D). A and C, DNA binding activity was measured in gel shift assays using ssDNA (20 fmol) as substrates. Complexes were separated on a 5% native polyacrylamide gel. The bands indicated by brackets in lanes 3– 8 (A) or lanes 3–7 (C) represent the Cdt1-Mcm4/6/7-DNA complex. B and D, DNA helicase assays were conducted as in A and C, respectively, except that the partial heteroduplex substrate (10 fmol) was used. Because the purified Cdt1 protein from the insect cell contained 2 mm ATP, complement buffer was added to maintain the final reaction mix as follows: 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 60 mm sodium acetate, 6% glycerol, 0.3 mm EDTA, 0.6 mm DTT, 20 mm 2-mercaptoethanol, 0.006% Triton X-100, 0.25 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 11.2 mm MgOAc, and 11.2 mm ATP. Half of the reaction was incubated at 30 °C for the gel-shift assay and the remainder was incubated at 37 °C for the DNA helicase assay (A and B). In A, the extent of DNA binding with Mcm or Tag alone was taken as 1, and the relative efficiency of DNA binding in the presence of various amounts of Cdt1 protein is presented for each helicase. In B, the level of the displaced oligonucleotide was quantified, and that with Mcm or Tag alone was taken as 1. The relative level of DNA unwinding in the presence of various amounts of Cdt1 protein is presented for each helicase. D, heat-denatured substrates.
