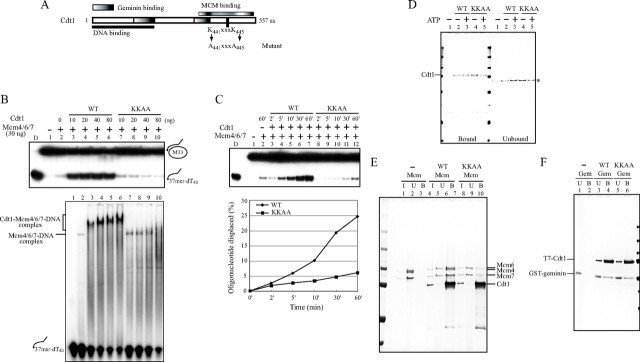
FIGURE 6.
Biochemical characterization of Cdt1 (KKAA) mutant protein. A, schematic drawing of domain structures of Cdt1, and the mutagenized amino acids. B, using the identical amount of wild-type or KKAA Cdt1 protein, the effect on DNA binding (lower panel) and helicase (upper panel) activities of Mcm4/6/7 were examined. The proteins used were; 30 ng of Mcm4/6/7 and 10, 20, 40, and 80 ng of Cdt1. C, kinetics of helicase reactions using 30 ng of Mcm4/6/7 and 15 ng of Cdt1 (wild type or KKAA). D, pull-down assay was carried out with 50 ng of Cdt1 (wild type or KKAA) and 50 pmol of biotinylated oligonucleotide in the presence or absence of ATP. The bound (left half) and unbound (right half) proteins are shown. * indicates nonspecific bands. E, purified Mcm4/6/7 (200 ng) was mixed with the same amount (200 ng) of wild-type or KKAA T7-tagged Cdt1, and immunoprecipitation experiments were performed using T7-antibody beads as described under “Experimental Procedures,” except that beads were further washed twice with T7-wash buffer (4.29 mm Na2HPO4, 1.47 mm KH2PO4, 2.7 mm KCl, 137 mm NaCl, and 0.1% Tween-20, pH 7.3). F, purified geminin (200 ng) was mixed with same amount (200 ng) of wild-type or KKAA T7-tagged Cdt1, and immunoprecipitation experiments were performed using T7-antibody beads as described under “Experimental Procedures.” In D, E, and F, the samples were run on 4–20% SDS-PAGE, and the proteins were detected by silver staining. In E and F: I, input; U, unbound; B, bound. Cdt1 was overexpressed and purified from insect cells (B and C) or from E. coli (D, E, and F). The KKAA mutant did not promote the high molecular weight complex formation with Mcm at a higher concentration and did not stimulate the helicase activity of Mcm4/6/7. The interaction of the mutant Cdt1 with Mcm was significantly reduced, although it interacted with DNA and with geminin as efficiently as wild-type.