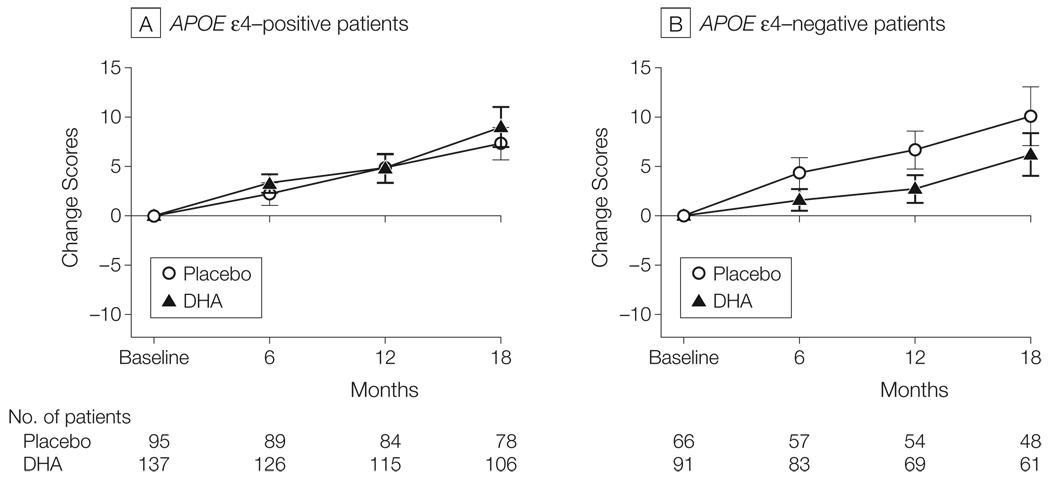
Figure 3.
Rate of Cognitive Change on Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS) Divided by Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Genotype
Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. The linear mixed-effects analysis finds no effect of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on the rate of ADAS-cog change in APOE ε4–positive participants but when the analysis is confined to APOE ε4-negative participants, the rate of change in ADAS-cog is slower in participants treated with DHA than in participants treated with placebo (linear mixed-effects model: P = .03). There was no evidence of a DHA effect on Clinical Dementia Rating sum of boxes, Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study activities of daily living, or Neuropsychiatric Inventory on rates of brain atrophy (see “Results” section).