Figure 1.
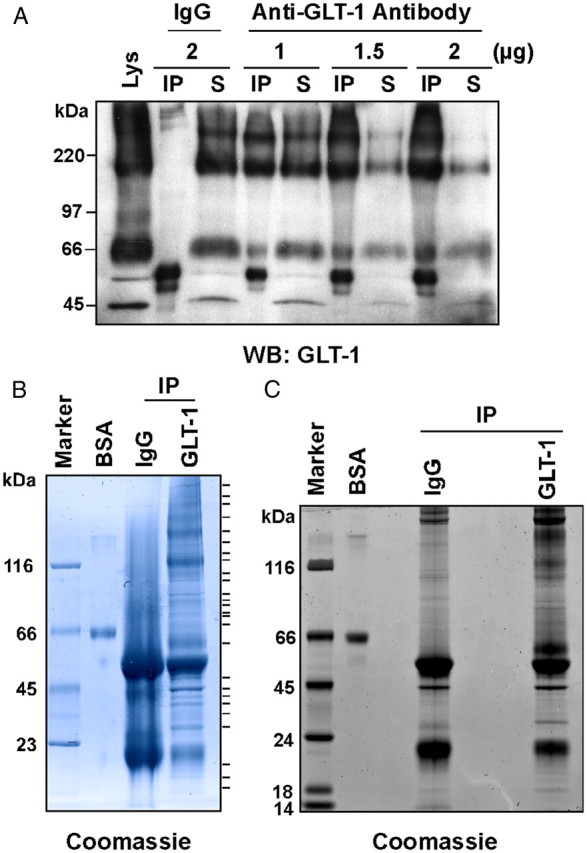
Immunoaffinity purification of GLT-1 from rat cortex. A, The amount of GLT-1 antibody required to deplete the supernatant of GLT-1 protein was optimized. Rat cortical lysates (50 μg protein) were immunoprecipitated with rabbit IgG antibody or increasing amounts of GLT-1 antibody, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and probed for GLT-1. Equivalent percentages of the immunoprecipitate (IP) and corresponding supernatant (S) were loaded on the gel. As observed previously, GLT-1 migrates as a monomer with a molecular weight of ∼66 kDa and a trimer of ∼200 kDa (Haugeto et al., 1996). Using 2 μg of GLT-1 antibody, 70% of GLT-1 was immunoisolated from the cortical lysate. Cortical lysate (Lys) was also loaded (10 μg protein). B, Rat cortical lysates (1 mg protein) were immunoprecipitated with 40 μg GLT-1 antibody or rabbit IgG, resolved on a 4–12% Tris-Bis gel, and stained with Coomassie blue. Protein bands observed in the GLT-1 (but not in the IgG) immunoprecipitate were excised, digested with trypsin, and subjected to LC MS/MS analysis on a ThermoFinnegan LTQ mass spectrometer. Excised bands are marked to the right of the gel. BSA protein (0.5 μg) was loaded to assess relative abundance of proteins. C, Rat cortical lysates (1 mg protein) were immunoprecipitated with 40 μg GLT-1 antibody or rabbit IgG, resolved on a 4–12% Tris-Bis gel, and stained with Coomassie blue. Each lane (IgG and GLT-1) was excised into 20 equivalent fractions, digested with trypsin, and subjected to LC MS/MS analysis. BSA (0.5 μg) protein was also loaded.
