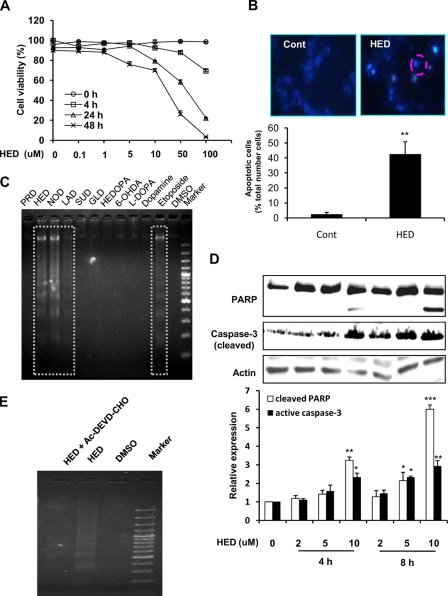
FIGURE 5.
Apoptosis induced by HED. A, dose- and time-dependent cytotoxicity of HED. SH-SY5Y cells were exposed to 0–100 μm HED for different retention times. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay. B, chromatin condensation in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 10 μm HED. The cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde, stained with Hoechst 33258, and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Upper left panel, control (Cont) cells staining. Upper right panel, HED-treated cells staining. Lower graph, statistical analysis of apoptotic cells. C, DNA fragmentation in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 25 μm HED or other samples for 12 h. Nucleosomal DNA fragmentation was visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis. D, PARP cleavage and active caspase-3 expression in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to 0–10 μm HED for 4 h and 8 h. The cleavage of PARP and expression of active caspase-3 were tested by Western blotting and statistically analyzed. E, effect of caspase-3 inhibitors on HED-induced DNA fragmentation. The inhibitor used was AC-DEVD-CHO. The SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 25 μm HED for 12 h in the presence or absence of inhibitor for 30 min. DNA fragmentation was visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis. All of the data are shown as the means ± S.D. (n = 3) (significantly different from control: * indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, and *** indicates p < 0.001).