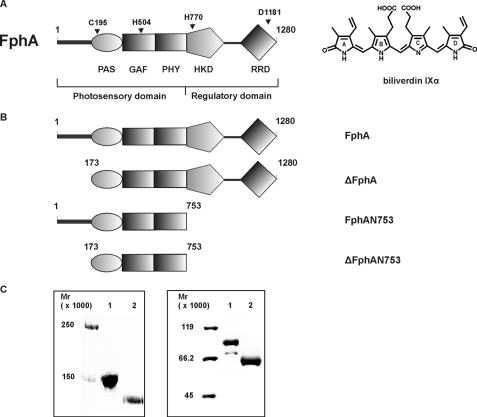
FIGURE 1.
A, domain organization of the fungal phytochrome FphA. Dark gray bar, variable N-terminal extension; PAS, PAS domain; GAF, GAF domain; and PHY, phytochrome domain (GAF-related domain) comprising the N-terminal photosensory domain. The C-terminal regulatory domain consists of histidine kinase domain (HKD) and response regulator domain (RRD). The following residues either essential for chromophore binding or coordination as well as for the signal output were assigned. C195, biliverdin IXα binding residue; H504, essential for chromophore coordination; H770, autophosphorylation site; and D1181, trans-phosphorylation site. The chemical structure of the covalently bound chromophore biliverdin IXα is shown on the right. B, domain structure of FphA variants. FphA, full-length protein; ΔFphA, protein without N-terminal variable extension; FphAN753, photosensory domain; ΔFphAN753, photosensory domain without N-terminal variable extension. C, SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant, Streptactin-affinity purified holo-FphA variants. Left panel: 1, holo-FphA; 2, holo-ΔFphA_H770A; right panel: 1, holo-FphAN753; 2, holo-ΔFphAN753. The samples were either loaded onto a 7.5% SDS-gel (left panel) or onto a 10% SDS-gel (right panel), and the proteins were visualized by staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue.