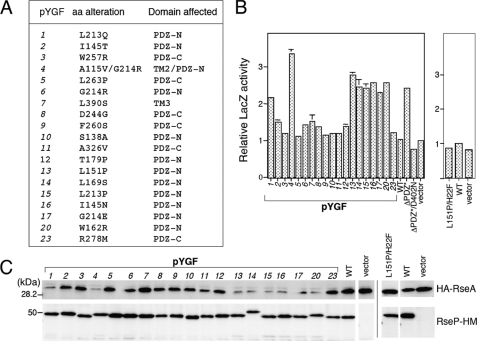
FIGURE 2.
DegS-independent proteolysis of RseA by the PDZ mutant forms of RseP-HM in vivo. A, amino acid alterations and the domains affected in the RseP-HM mutants isolated by the genetic screening. B, reporter LacZ activities induced by expression of the RseP PDZ mutants. Cells of TR71 (rpoHP3-lacZ) carrying the indicated pYGF plasmid, pKK11 (RseP-HM; WT), pKK131 (RseP(ΔPDZ*)-HM; ΔPDZ*), pKK135 (RseP(ΔPDZ*/D402N)-HM; ΔPDZ*/D402N), pSTD999 (RseP(L151P/H22F)-HM; L151P/H22F), or pTWV228 (vector) were grown at 37 °C in L medium (containing 10 g bacto-tryptone, 5 g yeast extract, and 5 g NaCl per liter; pH was adjusted to 7.2 by NaOH) and assayed for β-galactosidase activity. C, cellular levels of HA-RseA upon co-expression of the RseP PDZ mutants. pYGF plasmids, pKK11, pSTD999, and vector were introduced into AD1840/pSD691 (HA-RseA). Cells were grown at 30 °C in L medium containing 1 mm isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside and 1 mm cAMP for 2 h. Portions (containing ∼6 × 107 cells) of the cultures were withdrawn and mixed with an equal volume of 10% trichloroacetic acid for subsequent SDS-PAGE and anti-HA and anti-Myc immunoblotting analyses.