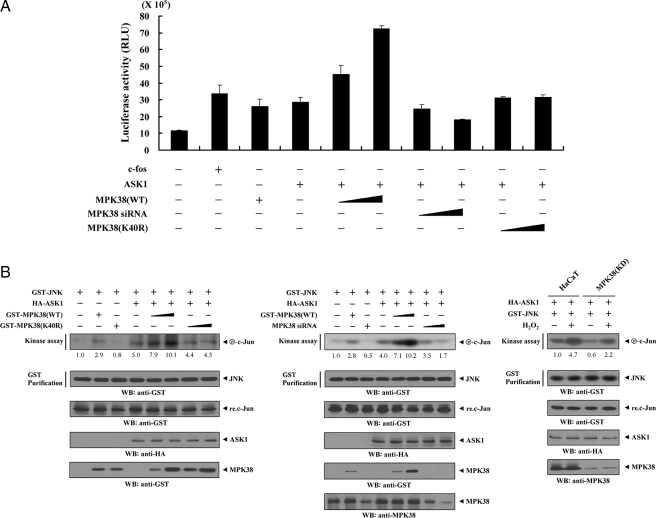
FIGURE 7.
Up-regulation of JNK-mediated transcription by MPK38. A, 293T cells were transfected with 0.2 μg of AP-1 luciferase plasmid and increasing amounts of wild-type (WT) and kinase-dead (K40R) forms of MPK38 (6 and 9 μg) and MPK38 siRNA 1 (50 and 200 nm) as indicated in the presence or absence of c-Fos (0.6 μg). Data shown are means (± S.E.) of three independent experiments. p < 0.05 relative to control; significance calculated by Student's t test. B, enhancement of JNK activity by MPK38. HEK293 cells were cotransfected using GST-JNK (1.5 μg) and HA-ASK1 (2 μg) in the presence or absence of increasing amounts of wild-type (WT) and kinase-dead (K40R) forms of MPK38 (6 and 9 μg) or MPK38 siRNA 1 (100 and 200 nm). An in vitro kinase assay for JNK activity was performed as described under “Materials and Methods.” The amounts of precipitated JNK and the expression level of ASK1 and MPK38 in total cell lysates were determined by immunoblot analysis using anti-GST and anti-HA antibodies. MPK38(KD) cells transfected with GST-JNK and HA-ASK1 were also precipitated using glutathione-Sepharose beads (GST Purification), and the precipitates were subjected to an in vitro kinase assay using c-Jun as a substrate to determine JNK activity (right). The relative level of JNK activity was quantitated by densitometric analyses, and fold increase relative to control HEK293 cells expressing JNK alone or untreated HaCaT cells expressing JNK and ASK1 was calculated. WB, Western blot.