FIGURE 4.
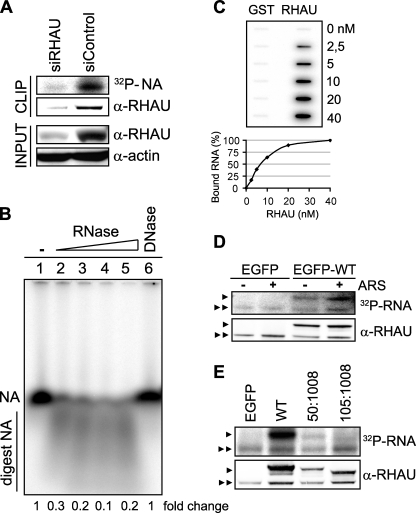
RHAU associates with RNA through its N terminus. A, CLIP method to identify interactions of RHAU with nucleic acids (NA). HeLa cells were transiently transfected with small interfering RNAs against RHAU (siRHAU) or luciferase (siControl). Cells were UV irradiated 72 h later and harvested. Immunoprecipitation was performed with a RHAU antibody. Bound nucleic acids were radiolabeled and detected as a band of ∼120 kDa corresponding to RHAU (lane siControl). However, this band was strongly reduced when endogenous RHAU was depleted (lane siRHAU). Western blot (INPUT) shows efficient RHAU depletion by small interfering RNAs against RHAU. Actin was used as a loading control. B, identification of associated nucleic acids as RNA. After immunoprecipitation, the nucleic acids bound to RHAU were isolated, radiolabeled, and treated with increasing concentrations (0.015, 0.15, 1.5, and 15 units) of RNase A and 1 unit of RQ1DNase. Lane1, isolated and non-treated nucleic acids(NA); lanes 2-5, isolated nucleic acids treated with increasing concentrations of RNase; lane 6, nucleic acids treated with DNase. -Fold changes in intensity ratio (NA/digest NA) are depicted relative to the intensity of non-treated nucleic acids in lane 1, set as 1. Note that nucleic acids are RNase-sensitive but DNase-insensitive. C, RHAU binds to RNA in vitro. 0, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, and 40 nm GST or GST-RHAU (RHAU) was incubated with 5,000 cpm 5′-end-labeled RNA for 30 min at 37 °C and filtered through nitrocellulose and nylon membranes. The percentage of bound RNA was plotted as a function of increasing concentration of GST-RHAU. Note that dose-dependent RNA binding was seen only with GST-RHAU. D, effect of stress on RHAU association with RNA in vivo. HeLa cells were transfected with EGFP alone or EGFP-WT (a full-length RHAU). Half were treated 24 h later with arsenite (0.5 mm for 45 min) followed by UV irradiation and radiolabeling of RHAU-associated nucleic acids. RHAU and associated RNA were analyzed by Western blotting and a phosphorimaging system to detect levels of protein expression and the amount of radiolabeled RNA, respectively. Note that the arsenite treatment (+) did not abolish or dramatically change the RNA binding activity of RHAU. ARS, arsenite. E, comparison of RNA binding activities of wild-type RHAU and its N-terminal deletion mutants. HeLa cells were transfected with EGFP, EGFP-WT, EGFP-(50-1008), or EGFP-(105-1008). Protein and associated RNA were analyzed as in A. Radioactivity of bound RNA was normalized to the expression levels of corresponding proteins. In sharp contrast to constant RNA binding of endogenous RHAU in each lane, N-terminal deletion mutants showed stepwise reduction of RNA interaction compared with WT. ▸, overexpressed EGFP-RHAU or its N-terminal deletion mutants; ▸▸, endogenous RHAU.