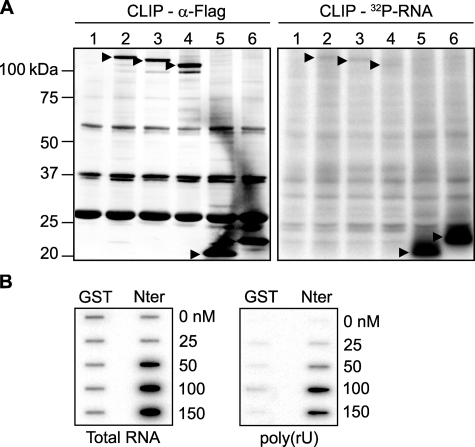
FIGURE 6.
The N-terminal RNA-binding domain is essential and sufficient for RNA interaction in vivo and in vitro. A, CLIP method to show RNA binding activity of the N-terminal 105 amino acid residues of RHAU. HeLa cells were transfected with an empty vector (lane 1), vectors expressing FLAG-tagged RHAU wild type (lane 2), or its fragments, (50-1008) (lane 3), (105-1008) (lane 4), (1-105) (lane 5), and (1-130) (lane 6). Cells were UV irradiated 24 h later, harvested, and immunoprecipitated by FLAG antibody. Bound RNA was labeled with [γ-32P]ATP and detected by a phosphorimaging system as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Left panel, Western blot of immunoprecipitated FLAG-tagged RHAU and its fragments. Right panel, bound RNA. The amount of associated RNA was normalized to the expression level of proteins.▸, FLAG-tagged RHAU and its fragments. B, the N terminus of RHAU binds to RNA in vitro. 0, 25, 50, 100, and 150 nm GST or GST-Nter (1-200 aa) was incubated with 10,000 cpm 5′-end-labeled total RNA (left panel) or poly(rU) (right panel) for 30 min at 37 °C and filtered through nitrocellulose and nylon membranes. Note that the dose-dependent RNA binding, both total RNA and poly(rU), was detected only with GST-Nter.