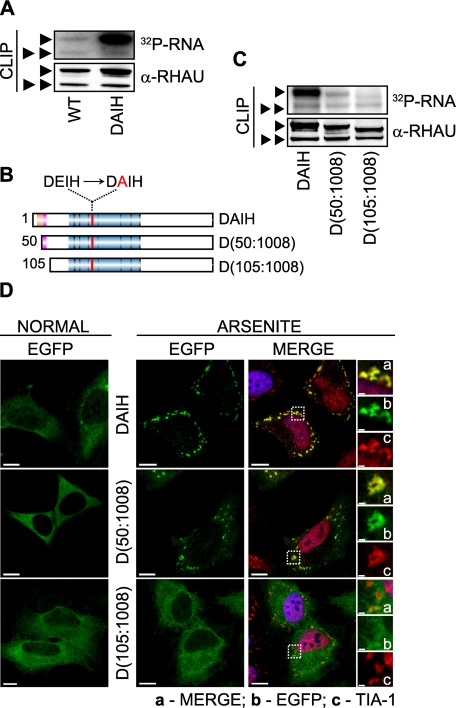
FIGURE 8.
Role of RHAU ATPase activity in RNA binding and retention of protein in SGs. A, RNA binding activity of WT and the ATPase-deficient RHAU mutant DAIH. Levels of RHAU-associated RNA were measured by CLIP as described under “Experimental Procedures” 24 h after transfecting HeLa cells with EGFP-fused WT or DAIH. The level of RNA bound to the DAIH mutant was much higher than that bound to WT. Note that the level of RNA bound to endogenous RHAU is comparable in cells expressing exogenous WT or DAIH. B, schematic representation of N-terminal deletion, DAIH mutants: EGFP-DAIH, EGFP-DAIH(50-1008) (D(50:1008)), and EGFP-DAIH(105-1008) (D(105: 1008)). C, comparison of RNA binding between mutants shown in B. HeLa cells were transfected with vectors expressing EGFP-DAIH, EGFP-DAIH(50-1008) (D(50:1008)), or EGFP-DAIH(105-1008) (D(105:1008)), and 24 h later the levels of RNA associated with these mutants and endogenous RHAU were assessed by CLIP as in A. Note that N-terminal deletion mutants show stepwise reduction of RNA binding compared with DAIH full length (such as WT and its deletion mutants in Fig. 4E). D, intracellular localization of EGFP-tagged DAIH mutants listed in B in control and arsenite-treated cells. Transfected HeLa cells were treated without (NORMAL) or with 0.5 mm sodium arsenite for 45 min. Images denoted MERGE are the merger of EGFP (green), TIA-1 (red), and DAPI (blue). Enlargements of boxed regions show merge (a), EGFP-tagged DAIH mutants (b), and TIA-1 (c). Bar, 10 μm (1 μmin enlargements). ▸, EGFP-tagged DAIH and its deletion mutants; ▸▸, endogenous RHAU.