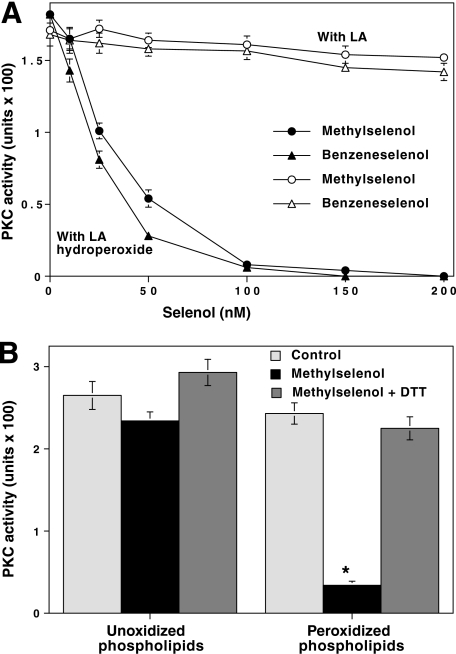
FIGURE 5.
Low concentration of methylselenol inactivates PKC bound to lipid peroxides. A, inactivation of PKC by methylselenol in the presence of linoleic acid hydroperoxide. Linoleic acid hydroperoxide was prepared from linoleic acid as described previously (87). Various concentrations of nascent methylselenol, prepared by mixing MSA and DTT (1:2 mol/mol) were incubated with PKCα in the presence of either linoleic acid (LA) or linoleic acid hydroperoxide (25 μm). This reaction was carried out in a total volume of 0.5 ml in microcentrifuge tubes with fitted rubber stoppers. The samples were incubated for 15 min at room temperature while shaking on an end-to-end rotator. Then the residual PKC activity was determined using histone H1 as the substrate. In some experiments, methylselenol was replaced with benzeneselenol. B, methylselenol inactivates PKC bound to peroxidized phospholipid vesicles. Phospholipid vesicles (phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine (4:1)) were prepared for binding PKC. These vesicles were subjected to peroxidation as described previously (88). PKCα was incubated with 50 nm methylselenol in the presence of either unoxidized phospholipids or oxidized phospholipids. CaCl2 (1 mm) was included to facilitate the binding of PKC to lipid vesicles. Incubations and PKC determinations were carried out as in A. The values are expressed as mean ± S.E. of triplicate estimations. The values obtained from methylselenol in the presence of peroxidized lipids were compared with the values of the respective controls obtained from peroxidized lipids alone (*, p < 0.01, evaluated by paired t test).