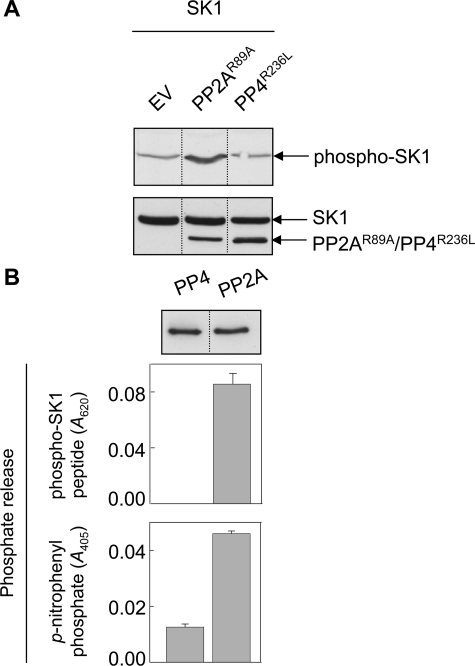
FIGURE 6.
Regulation of cellular phospho-SK1 levels by PP2A. A, HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding FLAG-tagged SK1 and HA-tagged catalytically inactive mutants of PP2Ac or PP4c (PP2AcR89A or PP4cR236L, respectively), or the corresponding empty vector (EV). Cell lysates were immunoblotted with an antibody recognizing phospho-SK1 (upper panel). Total SK1 and phosphatase expression levels were confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG and anti-HA antibodies, respectively (lower panel). Results are representative of three independent experiments. B, HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding HA-tagged PP4c or PP2Ac and the phosphatases immunoprecipitated from cell lysates using an anti-HA antibody. Immunoprecipitations with no primary antibody were used as negative controls. Immunoprecipitated phosphatases present in the phosphatase assays were detected by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody (representative blot, upper panel). Immunoprecipitated phosphatases were incubated with either phospho-SK1 peptide for 30 min, and reactions were terminated with Malachite Green stop solution prior to reading the absorbance at 620 nm (middle panel), or incubated with p-nitrophenyl phosphate for 45 min prior to reading the absorbance at 405 nm (lower panel). Data are expressed as the phosphate release, relative to the negative controls. Data for the phospho-SK1 peptide substrate are mean (±S.E.) from three independent experiments, and data for the p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate are mean (±range) from two independent experiments. All analyses in each experiment were performed in duplicate. The dividing lines indicate where lanes have been spliced to simplify viewing, but results in each panel are from a single experiment.