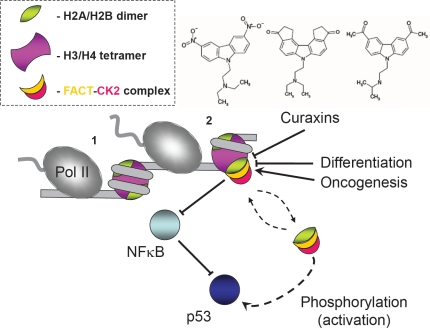
Figure 1. FACT as a regulatory hub in cell differentiation and carcinogenesis.
As RNA polymerase II (Pol II) encounters nucleosomes (1) and uncoils nucleosomal DNA from core histones (2), FACT interacts with the H2A/H2B dimer and facilitates transcription through chromatin. Binding of FACT results in cell growth inhibition through inhibition of NK-κB and activation of p53 by CK2 phosphorylation. Curaxins intercalate into the DNA, induce a conformational change in the DNA and interfere with recruitment of FACT.