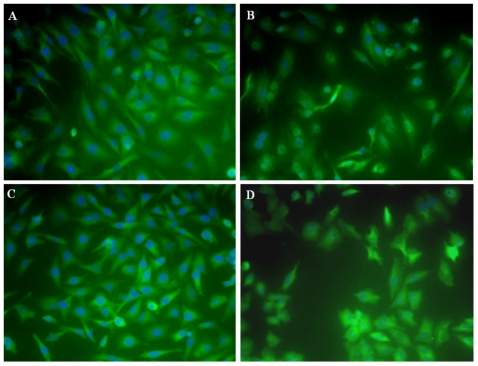
Figure 2. Effect of boronic acid treatment on the nuclear or cytoplasmic localization of NF-κB.
Nuclear stain DAPI is shown in blue, while the NF-κB is represented by green. Visible blue nuclei surrounded by green indicate cytoplasmic NF-κB, while obliteration of the blue by green signal in the nucleus indicates nuclear NF-κB. (A) Untreated control, cytoplasmic NF-κB (B) Positive control, nuclear translocation of NF-κB in cells treated with LPS, (C) Treatment with 2,4-ditertbutoxypyrimidine-5-yl-boronic acid (80 nM, 2 hrs.), predominantly cytplasmic NF-κB and (D) Treatment with 5-isoquinoline-boronic acid (80 nM, 2 hrs.), predominantly nuclear NF-κB.