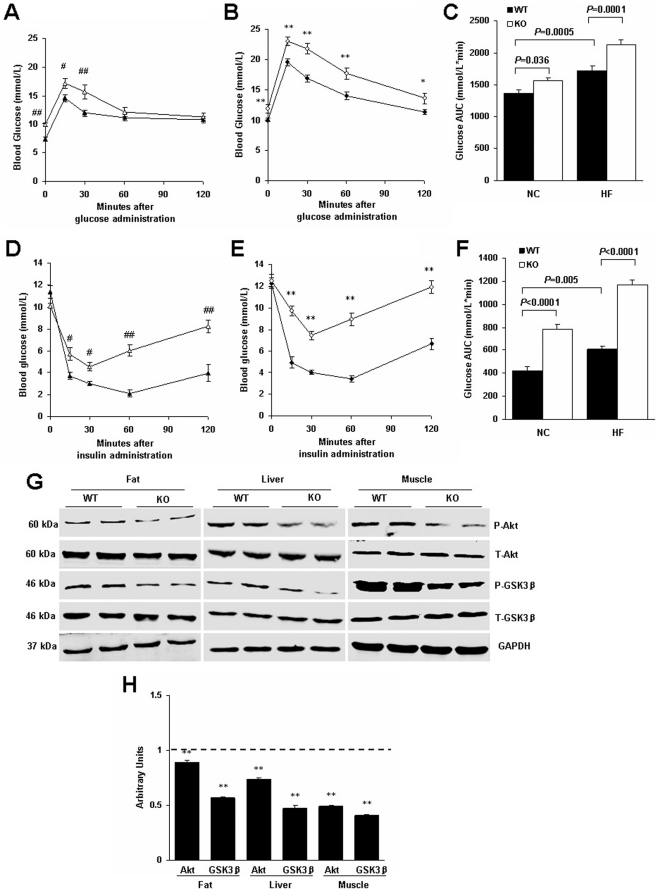
Figure 6. RGS5 deletion resulted in decreased peripheral insulin sensitivity and suppressed the Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway in mice fed an HF for 24 weeks.
A,B,C Blood glucose levels during GTT were determined at the indicated time points after i.p. injection with a bolus of glucose in WT and KO mice fed an NC (A) and HF (B) and corresponding AUC (C) (n = 6–8). D,E,F Blood glucose levels during ITT were determined at the indicated time points after i.p. injection with a bolus of insulin in WT and KO mice fed an NC (D) and HF (E) and corresponding AUC (F) (n = 6–8). G Phosphorylation levels of proteins related to insulin signaling in the visceral adipose tissue, liver and gastrocnemius muscle of WT and KO mice (n = 6). H Quantitative measurements of p-Akt and p-GSK3β protein relative to their total protein between WT mice (a dotted line at value 1) and KO mice (black). Values represent means ± SEM. #p<0.05 and ##p<0.01 compared with WT mice fed an NC; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared with WT mice fed an HF.