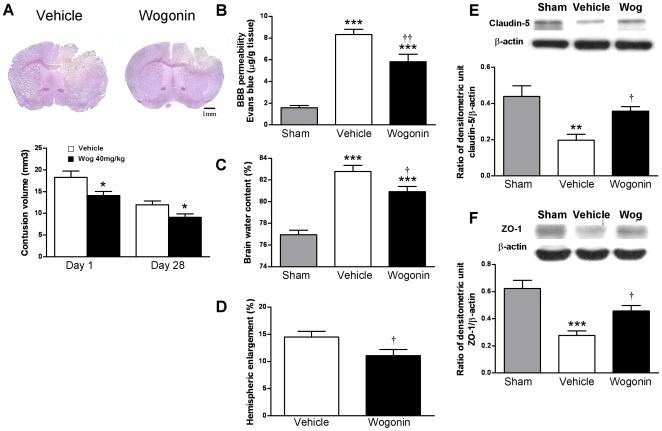
Figure 2. Effects of 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin treatment on cortical contusion volume, brain edema, and BBB permeability.
(A) Representative cresyl violet-stained brain sections of vehicle- and 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin-treated mice 1 day post-TBI showing hypointense regions immediately below the impact site in the cortex. Scale bar is 1 mm. Quantification showed significantly smaller contusion volumes in wogonin-treated mice compared with vehicle-treated mice at days 1 and 28 post-TBI. (B) Wogonin-treated mice showed a significant decrease in the concentration of Evans blue (EB) in the ipsilateral hemisphere compared with vehicle-treated mice at day 1. (C) Brain water content in the ipsilateral hemisphere of 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin-treated mice was significantly lower than in vehicle-treated mice at day 1. (D) At day 1, hemispheric enlargement was significantly smaller in mice treated with 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin than in vehicle-treated mice. (E, F) Treatment with 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin also reversed TBI-mediated reduced expression of claudin-5 and zonula occludens 1 in traumatic cortical areas of the ipsilateral hemisphere at day 1 following TBI, as measured by western blot. Values are presented as mean ± SEM; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus vehicle-treated injured mice. † P<0.05, †† P<0.01 for the 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin-treated mice versus vehicle-treated mice. (n = 8 mice/group for cresyl violet staining and hemispheric enlargement, n = 7 mice/group for brain EB, brain water content, and western blot).