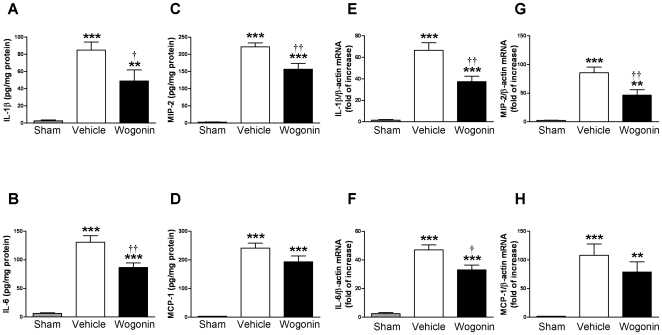
Figure 5. Effects of 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin treatment on protein and mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines.
(A, B, C, D) Bar graphs of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2, and monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 protein concentrations in the ipsilateral cortices of sham control, vehicle-treated, and 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin-treated mice at day 1 post-injury. Wogonin significantly attenuated injury-induced increases in IL-1β, IL-6, and MIP-2 protein concentrations, but had no effect on MCP-1 protein concentration compared with vehicle-treated TBI mice. (E, F, G, H) Bar graphs demonstrating IL-1β, IL-6, MIP-2, and MCP-1 mRNA expression in the ipsilateral cortices of sham control, vehicle-treated, and 40 mg·kg−1 wogonin-treated mice 6 h post-injury. Wogonin significantly inhibited injury-induced expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and MIP-2 mRNA in the ipsilateral cortices. There was no significant difference in MCP-1 mRNA transcript levels between the wogonin-treated and vehicle-treated groups of mice subjected to TBI. Values are presented as means ± SEM; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 versus sham control, and † P<0.05, †† P<0.01 for wogonin-treated mice versus vehicle-treated TBI mice (n = 7 mice/group).