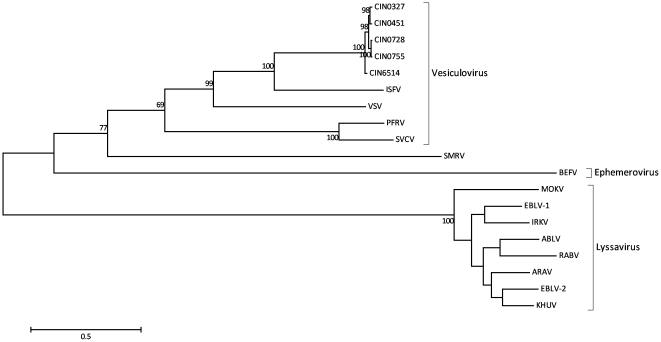
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of the whole genomes of the CHPV isolates and other rhabdoviruses using the Maximum likelihood method as implemented in MEGA. v.5.05.
Bootstrap values greater than 60% are indicated at the appropriate nodes. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Abbreviations: CHPV (Chandipura virus; acc nos. GU212856.1-58.1 [CIN0327, CIN0451, CIN0751], GU190711.1 [CIN0728], CIN6514 [deduced 1965 CHPV sequence]); ISFV (Isfahan virus; acc. no. AJ810084.2); VSV (vesicular stomatitis virus; acc. no. NC_001560.1); PFRV (pike fry rhabdovirus; acc. no. FJ872827.1); SVCV (spring viraemia of carp virus; acc. no. DQ097384.2); SMRV (Scopthalmus maximus rhabdovirus; acc. no. HQ003891.1); BEFV (Bovine Ephemeral fever virus; acc. no. AF234533.1); MOKV (Mokola virus; acc. no. NC_006429.1); EBLV-1 (European bat lyssavirus-1; acc. no. EU293112.1); IRKV (Irkut virus; acc. no. EF614260.1); ABLV (Australian bat lyssavirus; acc. no. AF418014.1); RABV (rabies virus; acc. no. GQ918139); ARAV (Aravan virus; acc. no. EF614259.1); EBLV-2 (European bat lyssavirus-2; acc. no. NC_009528.1); KHUV (Khujand virus; acc. no. EF614261.1).