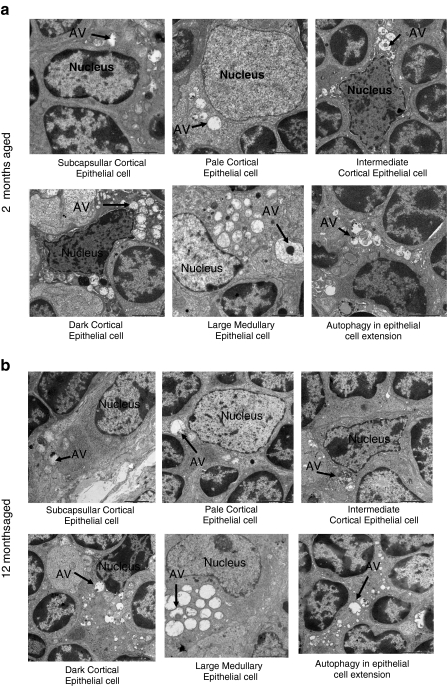
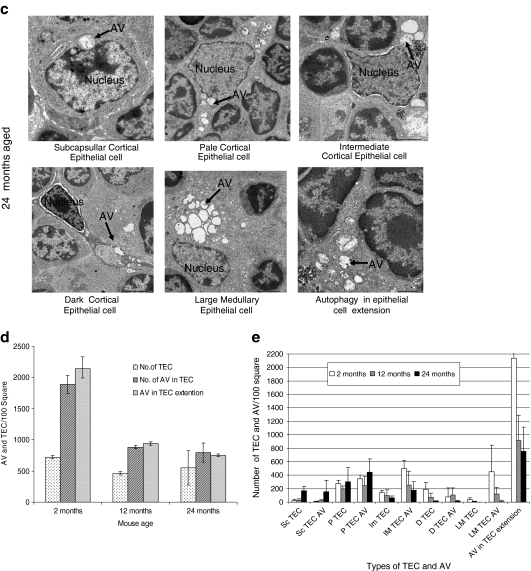
Fig. 4.
Ultrastructure analysis for thymic epithelial cells for autophagy. Electron micrograph (×2,500) of thymus tissues from a 2-, b 12-, and c 24-month-old C57BL/6J ♀ mice. Seventy-nanometer ultrathin sections were stained with uranyl acetate and lead stain solution. They were observed under the transmission electron microscope and photographed at ×2,500. Arrow marks indicate the autophagic structure in thymic epithelial cells. d The number of autophagic structure in thymic epithelial cells were enumerated under the electron microscope and presented as the number of thymic epithelial cells and autophagic structure per 100 squares in the copper grid. This figure shows the representative results from three independent experiments. e The number of autophagic structure in subcapsullar thymic epithelial cell (Sc TEC), pale thymic epithelial cell (P TEC), intermediate thymic epithelial cell (Im TEC), dark thymic epithelial cell (D TEC), large medullary thymic epithelial cell (LM TEC), and in epithelial cell extension was enumerated under the electron microscope and presented as the number of thymic epithelial cells and autophagic vacuole (AV) per 100 squares in the copper grid. This figure shows the representative results from three independent experiments