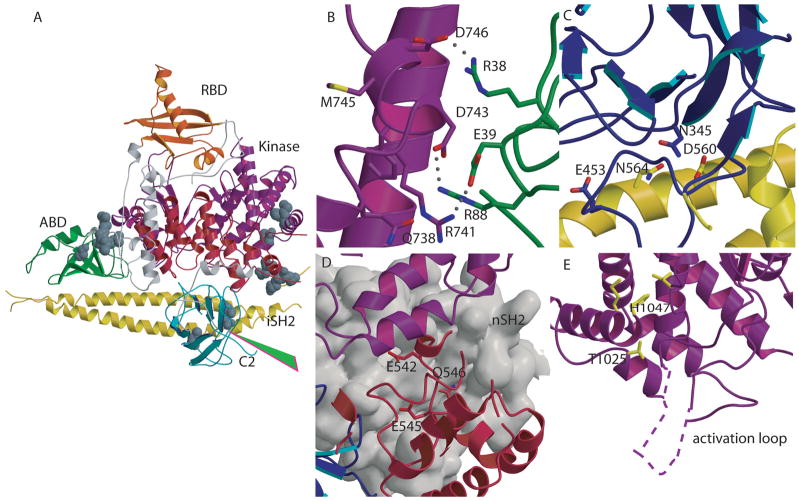
Fig. 4. Mutations in PIK3CA identified in human cancers.
(A) Location of representative mutations within p110α. Residues mutated in cancers are shown as CPK models. The start of the cancer associated truncation (residue 571 of p85) is shown by the green arrowhead. (B) Residues Arg38 and Arg88 , frequently mutated in cancers, are shown at the interface between the ABD and the kinase domains. (C) Contacts between the C2 and iSH2 domain in the p110α /p85 heterodimer. Asn345 of C2 and the residues within iSH2 (Asp560 and Asn564) with which it may interact are shown with a stick representation. (D) Residues in the helical domain commonly mutated in cancers (Glu542, Glu545, and Gln 546) are located at the interface with nSH2 (grey surface) in close proximity to the nSH2-kinase domain interface. (E) Mutations of the kinase domain, (Met 1043 and His1047), located near the C-terminal end of the activation loop, are shown in yellow. The portion of the activation loop between residues 941 to 950, not traced in the published structure, is shown as a dashed line.