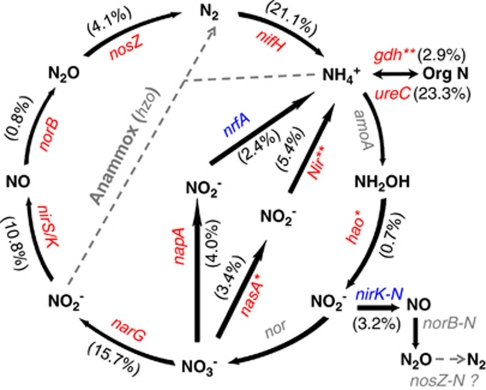
Figure 6.
The relative changes of the detected genes involved in the N cycle in oil plume. The signal intensity for each gene detected was normalized by all detected gene sequences using the mean. The percentage of a functional gene in a bracket was the sum of signal intensity of all detected sequences of this gene divided by the grand sum of signal intensity of the detected N cycle genes, and weighted by the fold change of the signal intensity of this gene in plume to that in non-plume. For each functional gene, red indicates that this gene had a higher signal intensity in plume than in non-plume and their significance was indicated with two stars (**) at P<0.01, whereas blue indicates that this gene had a lower signal intensity in oil-plume than in non-plume. Grey-colored genes were not targeted by this GeoChip, or not detected in those samples. It remains unknown if nosZ homologs exist in nitrifiers. Description of the genes: (a) gdh, encoding glutamate dehydrogenase, ureC, encoding urease responsible for ammonification; (b) nasA, encoding nitrate reductase, NiR, encoding nitrite reductase, responsible for assimilatory N reduction; (c) nifH, encoding nitrogenase responsible for N2 fixation; (d) narG encoding nitrate reductase, nirS and nirK-D (with denitrification activity), encoding nitrite reductase; nosZ, encoding nitrous oxide reductase, norB, encoding nitric oxide reducatse, responsible for denitrification (e) napA, encoding periplasmic nitrate reductase, nrfA, encoding c-type cytochrome nitrite reducatse, responsible for dissimilatory N reduction to ammonium; (f) hao, encoding hydroxylamine oxidoreductase, and nirK-N encoding nitrite reductase for nitrifiers (an indication of nitrification activity), responsible for nitrification.