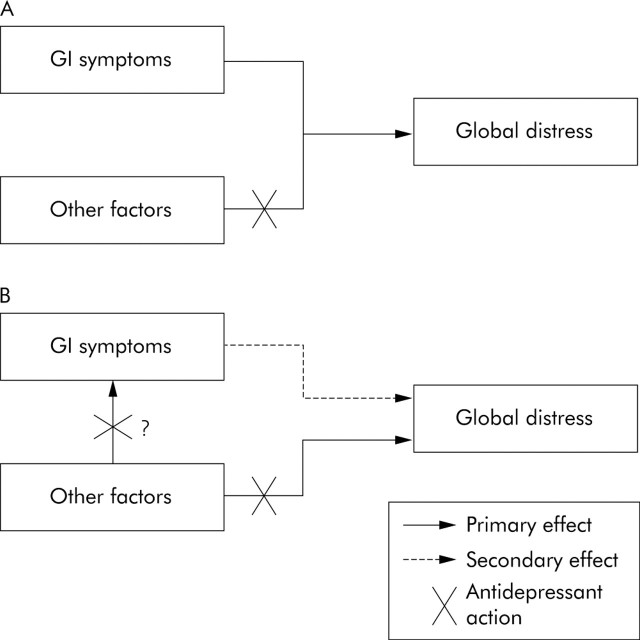
Figure 1.
New paradigms for understanding global impairment in functional gastrointestinal disorders and the potential effects of antidepressants. Factors other than gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms alone (for example, somatisation, other underlying neurophysiological mechanisms) may (A) coexist with functional gastrointestinal disorders or (B) underlie the presentation of functional gastrointestinal symptoms and have important independent effects on global well being. Antidepressants could block the independent effects of other factors on global well being or influence both the manifestation of functional gastrointestinal symptoms (for example, pain) and global well being through somewhat separate mechanisms. (Dual actions may be more representative of tricyclic antidepressants than selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.) The effect of antidepressants on global well being is not mediated through an action on gastrointestinal symptoms alone.