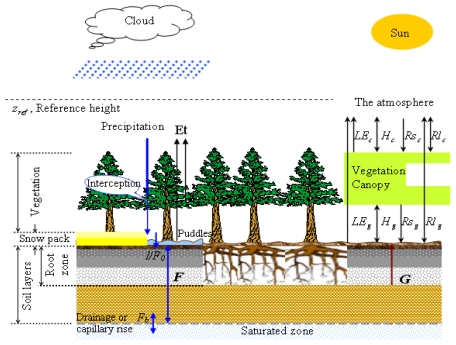
Figure 4.
Structure of the EASS model. Three components (soil, vegetation and the atmosphere) are considered in EASS, which are integrated with two interfaces. The right panel illustrated energy fluxes between these three components. LE, H, Rs, Rl, and G are the latent heat flux, sensible heat flux, shortwave radiation, longwave radiation, and soil conductive heat flux, respectively; the subscripts g and c present the energy fluxes at soil-canopy and canopy-atmosphere interfaces, respectively. The left panel describes soil water fluxes. The symbol F represents conductive water flux between soil layers, and F0 represents the incoming water flux from the surface to the top soil layer (i.e., the actual infiltration rate I), and Fb is the water exchange (drainage or capillary rise) between the bottom soil layer and the underground water [143].