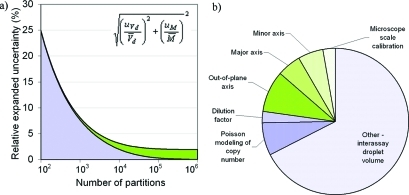
Figure 4.
Factors contributing to measurement uncertainty. (a) Theoretical relative expanded uncertainty of concentration considering only two factors: Type B partition volume component, Vd with a relative uncertainty of 1.0% (green), and uncertainty of the Poisson modeling of copy number per droplet, M,7 (mesh blue) calculated for the condition when 80% of the reactions are positive following digital PCR. This is close to the optimal percentage of positive reactions for minimizing the uncertainty of the copy number estimate, regardless of the number of reactions in the assay.10 The relative standard uncertainties of these two factors were combined (inset) and then multiplied by two to obtain the relative expanded uncertainty with a level of confidence of 95%. (b) Contributions to concentration uncertainty for a ddPCR data set comprising five replicate analyses from each of three independent gravimetric dilutions analyzed using assay 2 under simplex conditions (see Table 1 for details). This data set had a relative expanded uncertainty of only 4.2%, which was determined by multiplying the combined standard uncertainty (eq 8) by a coverage factor of 2.09 to provide a level of confidence of 95%. The contributions of the components of droplet volume (Type B components only) are indicated in green shading and the components of precision are indicated in blue shading. In this data set, a total of 190 433 droplets were accepted by the droplet reader and 19.1% of these droplets were positive.