Figure 2.
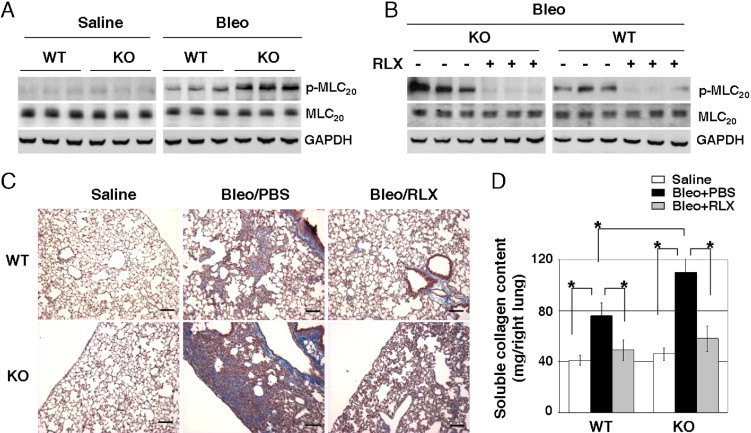
Relaxin (RLX) inhibits MLC20 phosphorylation and lung fibrosis in a bleomycin (Bleo)–induced mouse model. A: Lungs isolated from Bleo- and saline-treated RLX KO and WT mice were homogenized. Levels of phospho-MLC20 (p-MLC20) and total MLC20 in lung homogenates were determined by immunoblot analyses. GAPDH was used as the loading control. B: The RLX KO and WT mice were administered Bleo to induce lung fibrosis. At day 14 after lung injury, mice were given a continuous infusion of exogenous RLX or an equal volume of PBS (vehicle for RLX) through a s.c. implanted minipump for 7 days. Lungs were harvested at day 21. Levels of p-MLC20, total MLC20, and GAPDH were determined by immunoblot analyses. C: Masson's trichrome staining for collagen deposition in the saline and Bleo mouse groups treated with or without continuous infusion of exogenous RLX. Scale bars: 100 μm. D: Sircol-soluble collagen assay for mice treated as described in C (n ≥ 5 mice per group). *P < 0.01 for comparisons, as indicated.
