Figure 2.
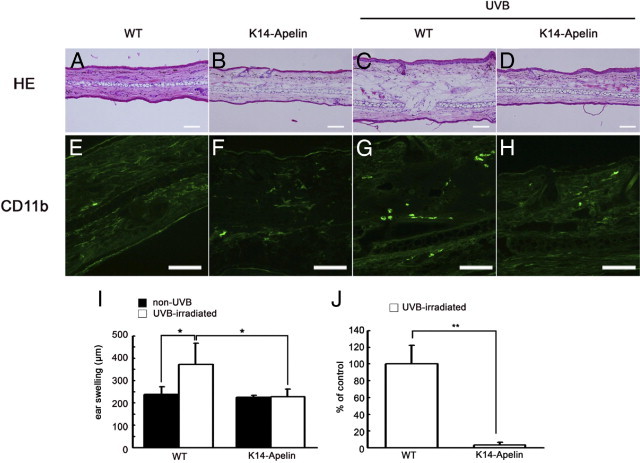
Apelin attenuates UVB-induced edema formation and inflammation. A–D: H&E staining revealed marked edema formation in the dermis of WT mouse ear skin (C), but K14-apelin mouse ear skin irradiated with UVB (D) was similar to non-UVB-irradiated skin (A and B). Scale bars: 100 μm. E–H: Immunofluorescence for CD11b (green) showed decreased macrophage infiltration in the dermis of K14-apelin mice ears (H), similar to non-UVB-irradiated mice (E and F), compared with WT mice irradiated with UVB (G). Scale bars: 100 μm. I: Skin thickness analysis indicated ear swelling in WT mice after UVB irradiation (*P < 0.05), but this swelling was attenuated in K14-apelin mice. *P < 0.05. J: The number of CD11b-positive cells was decreased in K14-apelin mice after UVB irradiation, compared with UVB-irradiated WT mice. *P < 0.01. Morphometric analyses (I and J) were performed using IP-LAB software version 4.0. Data are expressed as mean values ± SD (n = 3).
