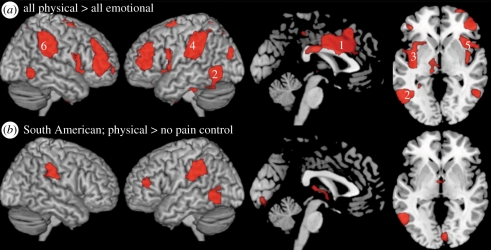
Figure 5.
Whole brain random effects analyses: brain regions involved in representing physical pain (PP). (a) Regions showing higher responses to stories about PP than emotional suffering, for all participants and targets, including (1) cingulate, (2) left lateral occipital, (3) left insula, (4) left secondary sensory, (5) right insula and (6) right secondary sensory regions. Functional activations corrected for multiple comparisons, p < 0.05; shown on a canonical template brain. (b) Many of the same regions are recruited more during stories about South American targets' PP, than for neutral control stories about South American targets, the no-pain control condition.