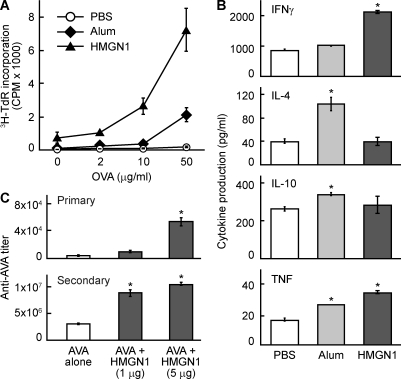
Figure 5.
HMGN1 promotes antigen-specific immune responses. 8-wk-old female C57BL/6 mice were immunized i.p. with OVA (50 µg/mouse), OVA + alum (3 mg/mouse), or OVA + HMGN1 (1 µg/mouse) on day 1 and boosted i.p. with OVA on day 14. On day 21, the spleens of immunized mice were removed, and single-cell suspension was evaluated for OVA-specific cellular immune responses. (A) Splenocytes were cultured in triplicate in a 96-well plate (5 × 105/0.2 ml/well) in the presence of specified concentrations of OVA for 4 d. The culture was pulsed with 1 µCi/well [3H]TdR for the last 18 h before harvest for measurement of [3H]TdR incorporation. OVA-specific proliferation of splenocytes is shown as the mean cpm (±SD) of each group (n = 4). (B) Splenocytes were cultured in duplicate in a 48-well plate (2.5 × 106/0.5 ml/well) in the presence of 100 µg/ml OVA for 48 h, and cytokines in the supernatants were quantitated. Shown is the mean cytokine concentration (±SD) of each group (n = 4) of one experiment representative of three. *, P < 0.05 by ANOVA when compared with the PBS group. (C) A/J mice (n = 4, 10 wk old, female) were immunized i.p. with AVA (the licensed human anthrax vaccine in the US) in the absence or presence of HMGN1 at specified doses (1 or 5 µg/mouse) on day 1 and booster immunized i.p. on day 14. Sera were collected on day 10 and 20 for the measurement of primary and secondary antibody responses, respectively. The IgG specific for the PA of anthrax in the serum was quantitated by anti-PA ELISA. Shown is the geometric mean anti-PA titer (±SD) of each group of one representative experiment out of three. *, P < 0.05 by ANOVA when compared with the AVA alone group.