Figure 2.
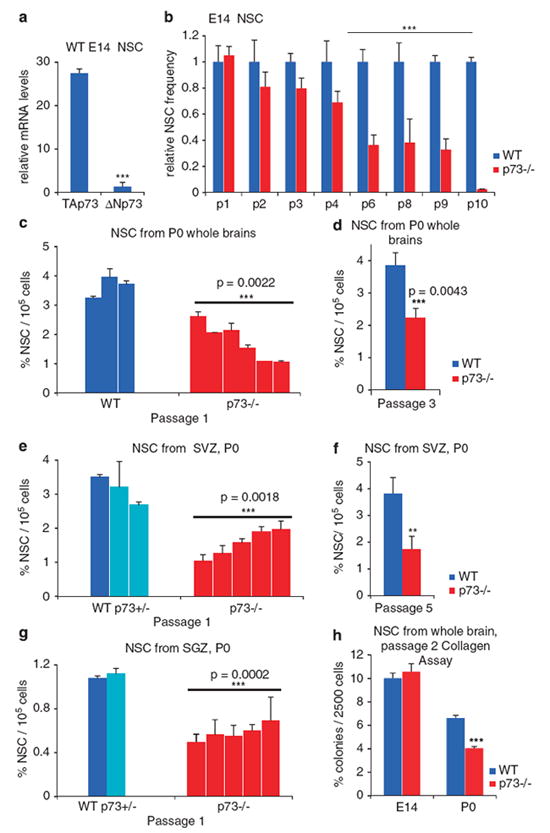
p73 is an essential regulator of neural stem cell survival and self-renewal. (a) Neurospheres derived from WT brains at E14 and P0 express both TAp73 and ΔNp73 isoforms. However, the levels of TAp73 are about 27-fold higher than those of ΔNp73, as determined by qRT-PCR. Values from whole brains at E14 are shown. See also Supplementary Figure 2. (b–g) p73−/− neural stem cells (NSC) at E14 and P0 exhibit self-renewal and maintenance defects. (b) Neurosphere assays derived from E14 forebrains. By passage 6, mutant cultures are severely impaired. p73−/− relative to WT neurosphere numbers from triplicate plates after each passage are indicated (n=3 each). (c–g) Neurosphere assays derived from P0 whole brains (c and d), the subventricular zone (SVZ; e and f) and hippocampus sub-granular zone (SGZ; g). Cultures derived from individual p73−/− pups from a representative litter of five independent litters with comparable results are shown (c, e and g). At P0, p73−/− cultures have severely impaired self-renewal, already evident at passage 1 (c, e and g) which persists with passaging (d, passage 3; and f, passage 5). Overall, the self-renewal capacity of p73−/− neural stem cells is reduced by 47% in whole brain (d), 56% in SVZ (f) and 48% in SGZ, compared with corresponding WT cultures. (h) Neural colony-forming cell assay in collagen. Passage 2 dissociated neurospheres derived from E14 and P0 whole brain WT and p73−/− mice were plated at clonal density (2500 cells/1.5 ml) in collagen. Number and size of newly formed colonies were evaluated after 21 days. A total of four mice/age/genotype were evaluated in triplicate in two independent experiments. Similar to the neuropshere assays, WT and p73−/− E14 cells produced a similar number of colonies, whereas p73−/− P0 showed ~ 50% decrease in the total number of colonies (P<0.0005)
