Figure 3.
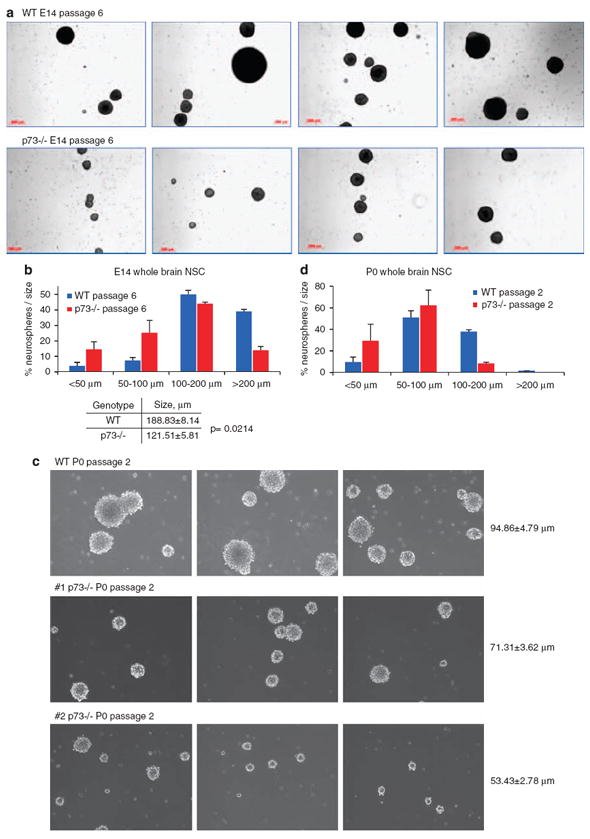
p73 is an essential regulator of neural stem cell proliferation. (a–d) Neurospheres from E14 and P0 p73−/− mice grow slower and are much smaller compared with WT neurospheres. (a) E14 neurospheres at passage 6. Representative images from WT and p73−/− littermates cultures are shown. (b) Size distribution of E14 neurospheres at passage 6 shown in (a). WT neurospheres tend to accumulate in the upper range, whereas a substantial number of p73−/− neurospheres accumulate in the lower range. At this stage, the frequency of their neural stem cells is also markedly reduced compared with WT (See Figure 2b). A total of >500 neurospheres were counted per genotype. (c) P0 neurospheres at passage 2. Most of the mutant cultures grow slower and form smaller spheres already at passage 2, compared with corresponding WT cultures. Some mutant variation exists. One WT and two mutant mice are shown as representative examples. (d) Size distribution of the P0 neurosphere shown in (c). WT neurospheres tend to accumulate in the upper range, whereas a substantial number of mutant neurospheres accumulate in the lower range. A total of >500 neurospheres were counted per genotype
