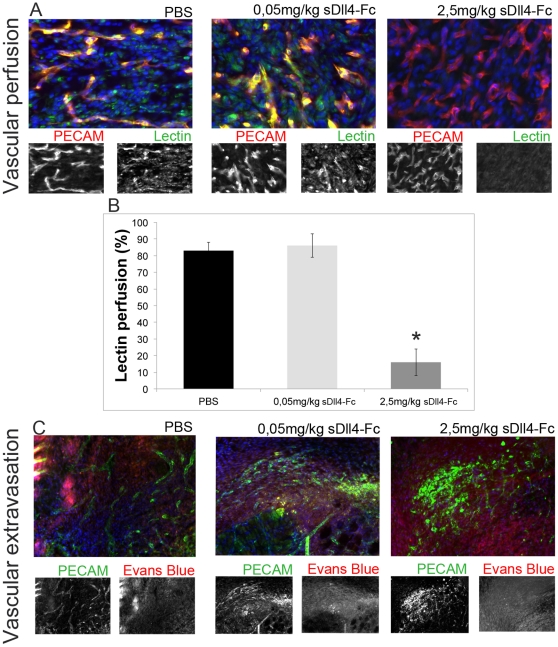
Figure 5. Low-dosage sDll4-Fc does not affect perfusion levels and leads to only a small increase in extravasation while higher dosages cause decreased perfusion and highly increased extravasation.
A) Representative anti-PECAM and anti-Lectin immunofluorescence images of neo-vasculature in granulation tissue of wounds treated with 0,05 mg/kg or 2,5 mg/kg compared with control mice injected with PBS, in day 6. B) The percentage of lectin-perfused blood vessels is similar between PBS- and 0,05 mg/kg sDll4-Fc injected mice but since vascular density is increased in the latter this result represents an effective increase in vascular function in the wound basin. Vascular perfusion is highly decreased in wounds of mice injected with 2,5 mg/kg sDll4-Fc. C) Representative anti-PECAM and Evans Blue immunofluorescence images of neo-vasculature in granulation tissue of wounds treated with 0,05 mg/kg or 2,5 mg/kg compared with control mice injected with PBS, in day 6. Vascular extravasation is highly increased in wounds of mice injected with 2,5 mg/kg sDll4-Fc but displays only a small increase in the case of 0,05 mg/kg sDll4-Fc injected mice. * In graphics represents p<0,05.