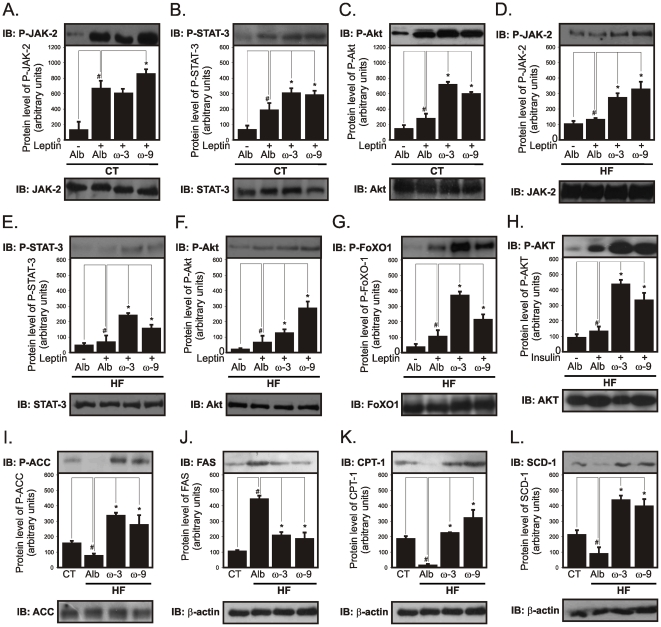
Figure 7. Effect of icv ω3 and ω9 on hypothalamic signaling.
Wistar rats fed on a regular chow (CT) or on a high-fat diet (HF) and icv cannulated were treated for seven days with diluent (albumin, Alb), ω3 or ω9 fatty acids. In addition, in some experiments, rats were acutely treated with a single dose of either leptin (2 µl, 10−6M: A-G) or insulin (2 µl, 10−6M: H) and then used in immunoblotting (IB) experiments. Specific antibodies against phospho-JAK2 (P-JAK2) (A and D), phospho-STAT3 (P-STAT3) (B and E), phospho-Akt (P-Akt) (C, F and H), phospho-FoxO1 (P-FoxO1) (G), phospho-ACC (P-ACC) (I), FAS (J), CPT-1 (K) and SCD-1 (L) were used to identify respective protein targets in hypothalamic tissue. Loading was evaluated by re-probing the membranes with anti-β-actin (J-L), anti-JAK2 (A and D), anti-STAT3 (B and E), anti-Akt (C, F and H), anti-FoxO1 (G) or anti-ACC (I). In A-H, #p<0.05 vs. Alb (−), *p<0.05 vs. Alb (+); in I-L, #p<0.05 vs. CT, *p<0.05 vs. Alb.