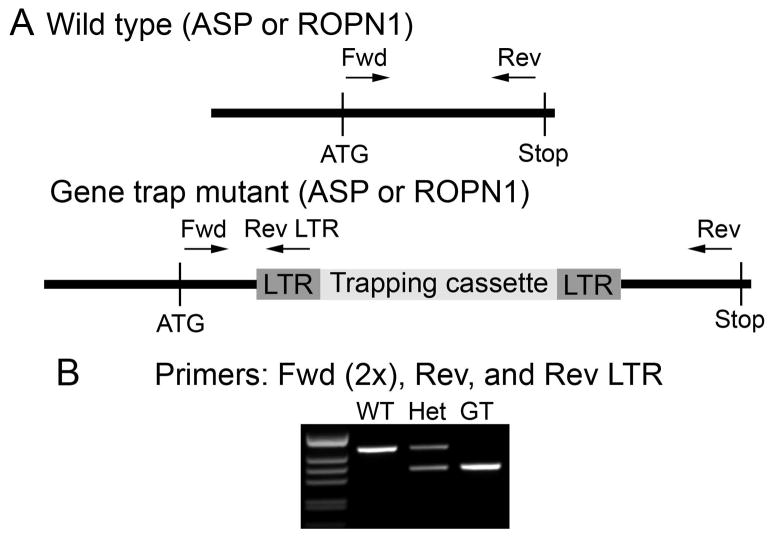
Figure 2. Genotyping scheme.
A. Mutations that interrupt expression at the protein level are contained in a trapping cassette that is flanked by identical LTR (long terminal repeat) regions. This construct is inserted in to the gene of interest (ASP or ROPN1 in this case). To identify animals containing the mutation, protein-specific primers to ASP and ROPN1 were designed to lie on opposite sides of the insertion site. A reverse LTR (Rev-LTR) primer sits on the mutant construct. B. When the Rev-LTR primer is paired with the protein-specific forward (Fwd) primer, a mutation-specific product is generated by PCR (band in GT lane). Protein-specific Fwd-Rev primer pairs will only generate a visible product in a wild type allele under our PCR conditions (band in WT lane, extension time is too low to allow formation of larger product in alleles that contain the mutant construct).