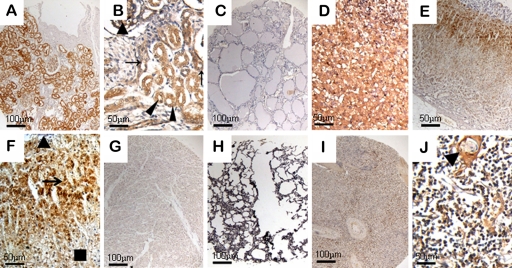
Figure 3.
Expression of ezrin in the genitourinary system, endocrine system, and other systems of human embryonic, fetal, and normal adult tissues. (A) Ezrin showed a strong staining in epithelial cells of the acinus renis (40×). (B) Ezrin was strongly positive in the acinus renis (triangles) and epithelial cells of the pars convoluta of the proximal tubule (arrowheads) and moderately positive in epithelial cells of the distal tubule (arrows) at 22 weeks’ gestation (200×). (C) Ezrin was undetectable in adult thyroid (40×). (D) At 12 weeks’ gestation, adrenal cortex and medulla showed strong reactivity (200×). (E) Ezrin was positive in the adult adrenal gland (40×). (F) In normal adult adrenal gland, ezrin immunoreactivity was exhibited in cells of the zona reticularis (arrow) and decreased in the zona glomerulosa (rectangle) and undetectable entirely in the medulla (triangle) (200×). Ezrin was undetectable in adult heart (G, 40×) and lung (H, 40×) but weakly positive in adult spleen (I, 40×). (J) Ezrin protein was present in subcapsular lymphocytes of the thymus and pronounced in Hassall’s corpuscle epithelial cells (triangle) (200×).