Figure 6.
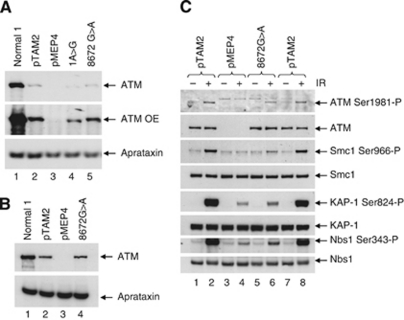
The p.Gly2891Asp protein has residual ATM kinase activity and a higher level of expression than the protein expressed from the c.1A>G mutation. (A) ATM protein without tags. ATM protein expression after zinc induction in the LCL stably transfected with pMEP4-ATM constructs was very low. Overexposure of the western blot showed that the c.1A>G derived protein (1A>G, lane 4) is truncated and accumulates to a lower level relative to the wt protein (pTAM2, lane 2) or the p.Gly2891Asp protein (8672G>A, lane 5). No ATM protein was expressed from the LCL transfected with vector alone (pMEP4, lane 3). Aprataxin was used as a loading control. (B) ATM protein with N-terminal tags. The induced levels of both wt protein (pTAM2, lane 2) and p.Gly2891Asp protein (8672G>A, lane 4) were increased when the ATM constructs were N-terminally tagged (compare with Supplementary Figure 2A). The p.Gly2891Asp (8672G>A) protein was expressed at a similar level to the wt protein. Aprataxin was used as a loading control. (C) Comparison of ATM kinase activity in lysates from LCLs stably transfected with pMEP4-ATM wt (pTAM2), pMEP4-ATM 8672G>A (8672G>A) or pMEP4 vector alone (pMEP4) all with N-terminal tags. Expression of the p.Gly2891Asp (8672G>A) protein (lane 5) was comparable to that of wt ATM (pTAM2, lanes 1 and 7). The p.Gly2891Asp (8672G>A) protein autophosphorylated Ser1981 following IR (lane 6) to levels comparable to that of ATM wt protein (lanes 2 and 8). Levels of IR-induced phosphorylation of ATM targets Smc1, KAP-1 and Nbs1 by the p.Gly2891Asp (8672G>A) protein were substantially lower than those for the ATM wt protein (lanes 2 and 8) but higher than for vector alone.