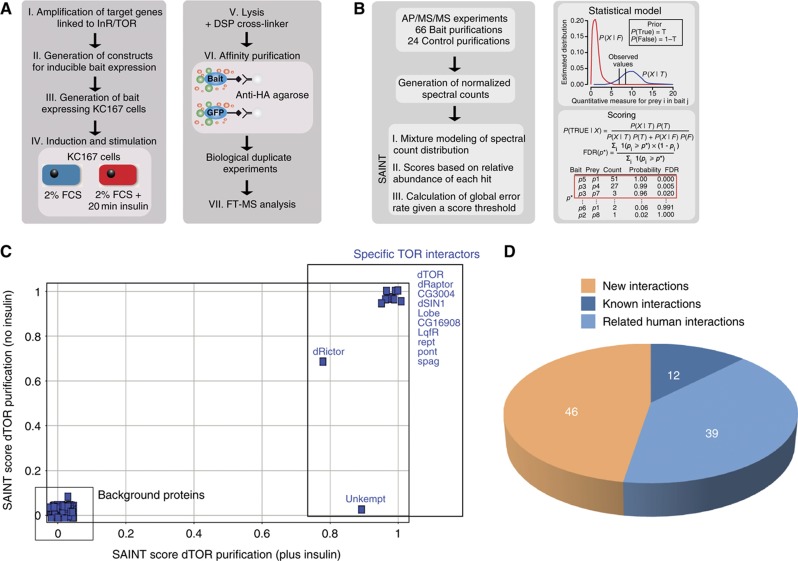
Figure 1.
Overview on the experimental workflow and data processing. (A) Experimental workflow. In all, 16 genes linked to dInR/TOR pathway were PCR amplified from cDNA pools. By recombinatorial cloning, the Drosophila ORFs were transferred into an in-house designed expression vector for inducible expression of epitope-tagged bait proteins. Bait expression was induced and cells were starved overnight in 2% FBS. Half of the cell population was exposed to 100 nM insulin for 20 min. The cells were lysed in the presence of DSP cross-linker and bait proteins were purified by anti-HA AP. All AP–MS/MS experiments were performed as two independent replicates. (B) Data processing of the AP–MS/MS data set for detection of specific PPIs using the SAINT algorithm. Following database search, spectrum counts for each identified protein were extracted from the LC–MS/MS data. Based on normalized spectrum counts, SAINT models the spectrum count distribution of each bait–prey interaction and calculates scores based on the relative abundance of each hit. In all, 24 independently control AP–MS experiments (using GFP as a bait protein) were performed in parallel to model false interaction distribution. (C) SAINT scores (data from two biological replicates) were plotted from dTOR purified in the absence (x axis) or the presence (y axis) of insulin to illustrate the specificity increase by the SAINT filtering approach. (D) Overlap with orthologous PPI data and known Drosophila PPIs. The PPI data obtained in this study were compared with available literature and database information covering known D. melanogaster and related Homo sapiens interactions (see also Materials and methods).