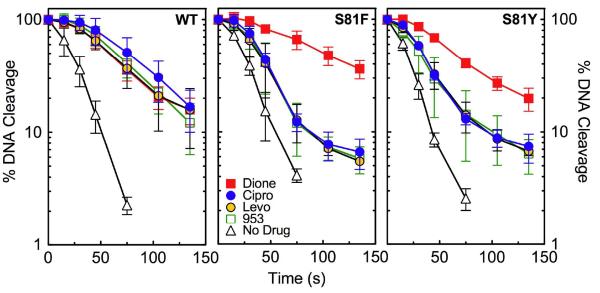
Figure 10.
Effects of quinolones and 8-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione on the DNA religation activities of wild-type, GrlAS81F, and GrlAS81Y topoisomerase IV. Results for assays carried out in the absence of drugs (No Drug, open triangle) or in the presence of ciprofloxacin (Cipro, blue circles), levofloxacin (Levo, yellow circles), CP-115,953 (953, open green squares), or 8-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione (Dione, red squares) are shown. DNA religation mediated by wild-type (WT), GrlAS81F (S81F), and GrlAS81Y (S81Y) topoisomerase IV are shown in the left, center, and right panels, respectively. Religation was assessed by monitoring the loss of double-stranded DNA breaks (linear product) over time. Cleavage at time zero was set to 100%. Quinolone concentrations were 20 μM in assays that examined wild-type topoisomerase IV and were increased to 200 μM in assays that examined the GrlAS81F and GrlAS81Y enzymes. The concentration of 8-methyl-quinazoline-2,4-dione was 20 μM in all assays. Reactions carried out in the absence of drugs replaced Mg2+ with Ca2+ in order to achieve readily quantifiable levels of DNA cleavage. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three or more independent experiments.